Unveiling the Underground: A Comprehensive Guide to Public Utilities Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Underground: A Comprehensive Guide to Public Utilities Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Underground: A Comprehensive Guide to Public Utilities Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Underground: A Comprehensive Guide to Public Utilities Maps
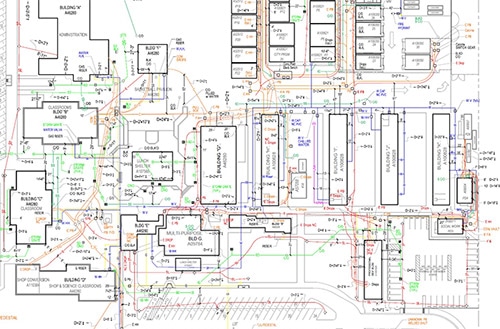
The bustling urban landscape we navigate daily is a complex tapestry woven with an intricate network of essential services. Beneath our feet lies a hidden infrastructure, a labyrinth of pipes, cables, and conduits that deliver electricity, gas, water, and communication. This underground world, crucial to our modern way of life, is often invisible, yet its accessibility and management are critical for efficient operations, safety, and sustainable development. This is where public utilities maps emerge as indispensable tools, providing a visual blueprint of this hidden infrastructure, enabling informed decision-making and streamlined operations.
Understanding the Essence: What are Public Utilities Maps?
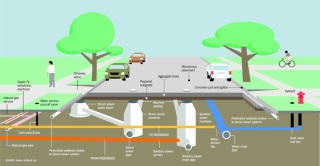
Public utilities maps, also known as underground utility maps or utility infrastructure maps, are detailed graphical representations of the location, type, and properties of public utilities infrastructure within a specific area. These maps serve as comprehensive guides, offering a visual overview of the intricate network of pipes, cables, and conduits that transport essential services like electricity, gas, water, telecommunications, and even sewage. They are essentially visual databases, containing critical information about:
- Location: Precise coordinates and depths of utility lines, pipes, and conduits.
- Type: Identification of specific utilities (e.g., electric, gas, water, sewer, fiber optic) and their associated infrastructure.
- Properties: Attributes like pipe diameter, cable size, voltage levels, and material type.
- Ownership: Identification of the utility company responsible for each infrastructure component.
- Historical Data: Records of previous excavations, repairs, and maintenance activities.
Beyond the Surface: The Crucial Role of Public Utilities Maps
Public utilities maps are not mere static diagrams; they are dynamic tools that play a pivotal role in various aspects of urban planning, infrastructure management, and public safety. Their significance extends across diverse sectors, including:
1. Construction and Development:
- Preventing Damage: Excavations and construction projects often pose a risk of damaging underground utilities. Public utilities maps provide accurate information on the location of these critical lines, minimizing the risk of accidental damage, costly repairs, and service disruptions.
- Efficient Planning: Maps help engineers and contractors plan construction projects effectively, ensuring infrastructure alignment and avoiding conflicts with existing utilities.
- Cost Optimization: By understanding the location of utilities, construction projects can be designed and executed more efficiently, reducing the need for unnecessary digging, rework, and delays.
2. Emergency Response and Disaster Management:
- Rapid Response: In the event of emergencies like natural disasters, power outages, or gas leaks, public utilities maps enable first responders to quickly locate and access utility infrastructure, facilitating efficient response and minimizing damage.
- Damage Assessment: Maps help assess the impact of disasters on utility networks, identifying damaged sections and prioritizing repairs for swift restoration of essential services.
- Risk Mitigation: Understanding the vulnerability of utility infrastructure to natural disasters and other hazards allows for proactive planning and mitigation measures to reduce risks and improve resilience.
3. Maintenance and Repair:
- Targeted Maintenance: Maps enable utility companies to prioritize maintenance efforts, focusing on areas with aging infrastructure or high risk of failure.
- Efficient Repairs: Accurate information on utility lines facilitates faster and more efficient repairs, minimizing service disruptions and ensuring timely restoration.
- Asset Management: Maps provide a comprehensive overview of utility assets, enabling effective tracking, inventory management, and planning for future infrastructure upgrades.
4. Urban Planning and Development:
- Sustainable Growth: By understanding the existing utility infrastructure, urban planners can make informed decisions regarding future development, ensuring adequate capacity for growing populations and expanding services.
- Infrastructure Optimization: Maps facilitate the identification of areas with limited utility capacity, enabling targeted infrastructure upgrades and expansion to meet future demands.
- Smart City Initiatives: Public utilities maps play a vital role in supporting smart city initiatives, enabling the integration of data from various sources to optimize resource management, enhance public safety, and improve overall city efficiency.
5. Environmental Protection:
- Leak Detection: Maps help identify leaks in water and gas pipelines, preventing environmental contamination and resource waste.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Maps provide valuable information for environmental impact assessments, ensuring that construction projects and infrastructure upgrades are carried out with minimal environmental disruption.
- Sustainable Infrastructure: By understanding the location and condition of utility infrastructure, planners can prioritize environmentally friendly materials and technologies, promoting sustainable development practices.
Beyond the Basics: The Evolution of Public Utilities Maps
The evolution of public utilities maps has mirrored the advancements in technology and data management. Traditional paper-based maps have given way to digital platforms, offering enhanced functionalities and accessibility. Modern public utilities maps are increasingly integrated with:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS technology allows for the creation of interactive, spatially referenced maps, enabling users to visualize utility infrastructure in relation to surrounding features, including buildings, roads, and terrain.
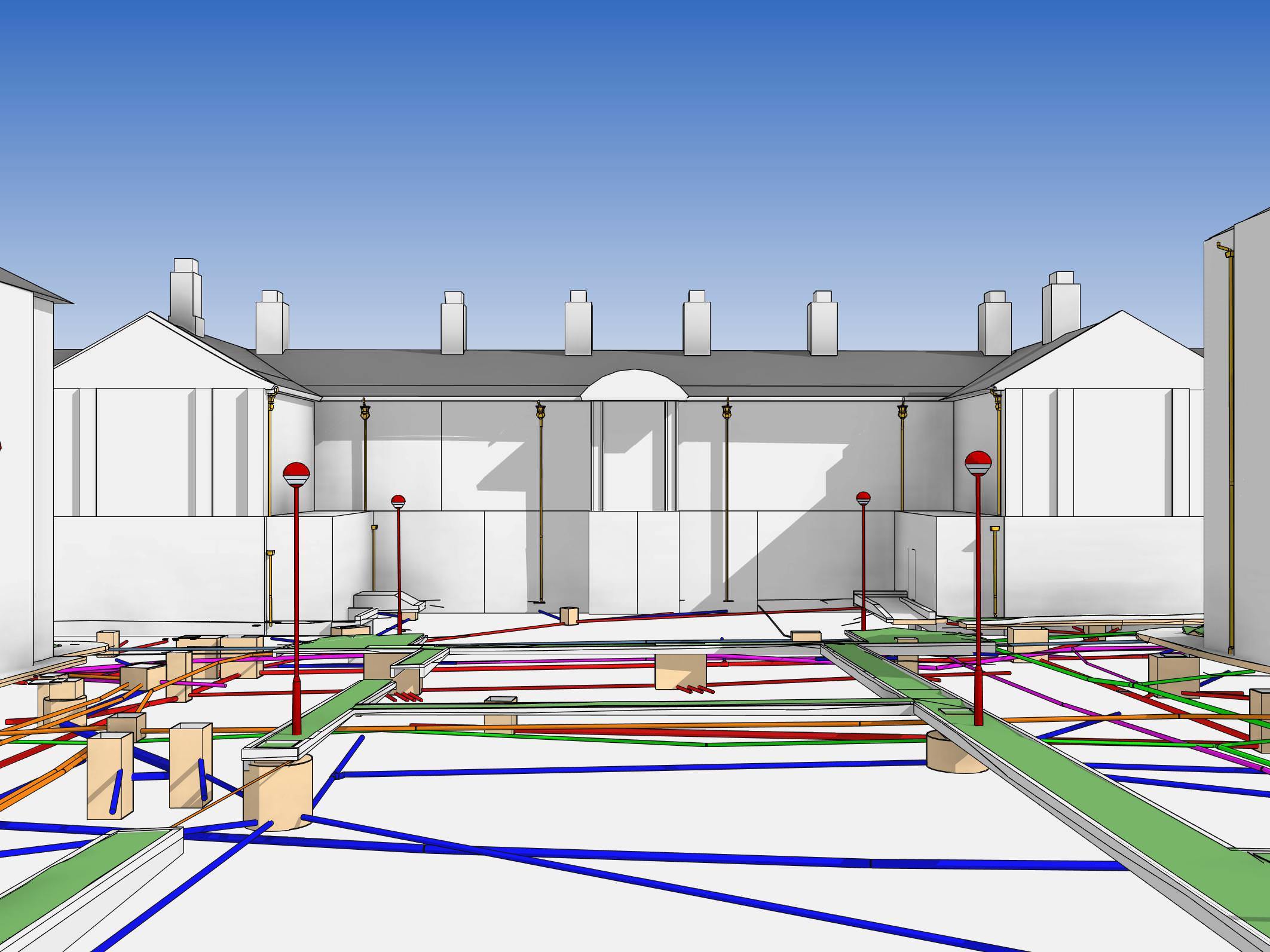
- 3D Modeling: Three-dimensional representations of utility infrastructure provide a more comprehensive understanding of the underground network, facilitating complex planning and analysis.
- Data Integration: Modern maps integrate data from multiple sources, including utility company databases, aerial imagery, and sensor networks, providing a holistic view of the infrastructure and its performance.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Cloud-based solutions offer greater scalability, accessibility, and collaboration capabilities, allowing multiple stakeholders to access and share utility map information seamlessly.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Public Utilities Maps
1. What are the different types of public utilities maps?
Public utilities maps can be categorized based on their scale, purpose, and data sources. Common types include:
- Planimetric Maps: Show the horizontal location of utilities, primarily used for construction and development planning.
- Profile Maps: Depict the vertical profile of utility lines, highlighting elevations and depths, essential for excavation and trenching.
- System Maps: Provide a comprehensive overview of the entire utility system, including interconnected components and flow paths.
- Asset Management Maps: Focus on individual utility assets, including their condition, age, and maintenance history.
2. Who uses public utilities maps?
A wide range of stakeholders rely on public utilities maps, including:
- Utility Companies: For planning, maintenance, repairs, asset management, and emergency response.
- Construction Companies: For project planning, excavation, and avoiding damage to utilities.
- Government Agencies: For urban planning, development, and infrastructure management.
- Emergency Responders: For locating utilities during emergencies and facilitating efficient response.
- Private Developers: For planning construction projects, ensuring compliance with utility regulations.
3. How can I access public utilities maps?
Access to public utilities maps varies depending on the jurisdiction and utility company. Some municipalities and utility companies provide online access to their maps, while others may require a formal request or subscription.
4. What are the benefits of using public utilities maps?
- Enhanced Safety: Preventing damage to underground utilities and ensuring public safety.
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlining construction, maintenance, and repair operations.
- Reduced Costs: Minimizing damage, rework, and service disruptions.
- Sustainable Development: Promoting responsible infrastructure planning and environmental protection.
5. What are the challenges associated with public utilities maps?
- Data Accuracy: Maintaining accurate and up-to-date information is crucial, requiring continuous updates and verification.
- Data Sharing: Sharing data between different stakeholders can be challenging due to privacy concerns and data security protocols.
- Accessibility: Ensuring widespread access to maps, particularly for smaller communities and developing countries.
- Cost and Resources: Developing and maintaining comprehensive public utilities maps can be resource-intensive.
Tips for Effective Utilization of Public Utilities Maps:
- Verify Data Accuracy: Ensure the maps are updated regularly and reflect the current state of the utility infrastructure.
- Utilize Multiple Sources: Combine information from different sources, including utility company databases, aerial imagery, and field surveys.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Encourage communication and data sharing between utility companies, contractors, and government agencies.
- Invest in Technology: Embrace GIS, 3D modeling, and cloud-based platforms for enhanced data management and visualization.
- Promote Public Awareness: Educate the public on the importance of public utilities maps and the need to protect underground infrastructure.
Conclusion: A Foundation for a Sustainable Future
Public utilities maps are not simply tools for managing underground infrastructure; they are fundamental to creating a safe, efficient, and sustainable urban environment. By providing a clear understanding of the hidden network that powers our cities, these maps empower decision-makers, planners, and engineers to make informed choices that promote economic growth, environmental protection, and public safety. As we continue to navigate the complexities of urban development, public utilities maps will remain essential guides, ensuring that the essential services we rely on remain accessible, reliable, and resilient for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Underground: A Comprehensive Guide to Public Utilities Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!