Unveiling the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Cloud Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Cloud Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Cloud Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Cloud Maps

In the vast expanse of the Earth’s atmosphere, clouds play a pivotal role in shaping our climate, influencing weather patterns, and impacting life on our planet. Understanding the dynamics of these celestial formations is crucial for various fields, ranging from meteorology and aviation to agriculture and disaster preparedness. Enter satellite cloud maps, powerful tools that provide a real-time glimpse into the ever-changing tapestry of clouds across the globe.
What are Satellite Cloud Maps?
Satellite cloud maps are visual representations of cloud cover and distribution generated from data collected by satellites orbiting Earth. These maps utilize various sensors and imaging techniques to capture information about cloud types, altitudes, and densities. This data is then processed and presented in user-friendly formats, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of cloud patterns.
How do Satellite Cloud Maps Work?
The creation of satellite cloud maps involves a sophisticated interplay of technology and scientific principles:
-
Satellite Data Acquisition: Satellites equipped with specialized sensors, such as infrared and visible light cameras, continuously scan the Earth’s surface. These sensors detect variations in reflected sunlight and emitted infrared radiation, which provide insights into cloud properties.
-
Data Processing: The raw data collected by satellites is processed and analyzed using sophisticated algorithms. This involves identifying cloud features, classifying cloud types, and generating maps that depict cloud coverage and distribution.
-
Visualization and Interpretation: The processed data is then transformed into visual representations, often displayed as color-coded maps. These maps allow users to easily identify cloud patterns, track cloud movement, and assess the potential impact of cloud formations on weather and climate.
Types of Satellite Cloud Maps:
Several types of satellite cloud maps are available, each offering specific insights:
-
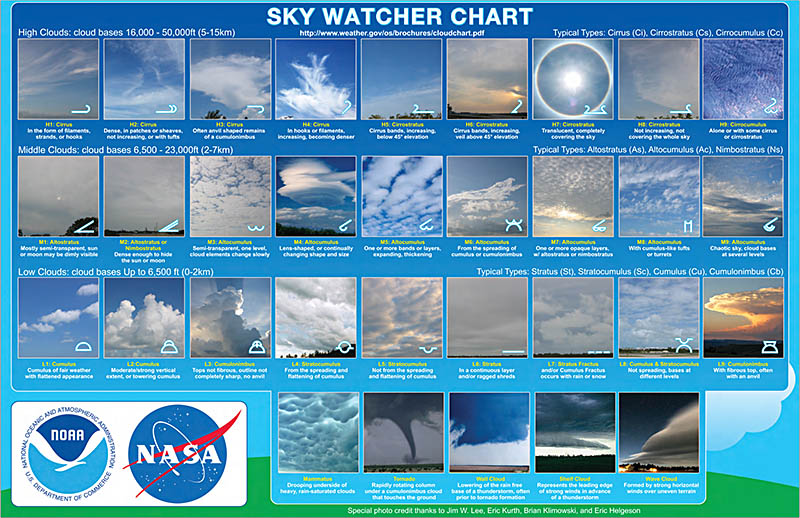
Infrared Cloud Maps: These maps utilize infrared radiation emitted by clouds to determine their temperature and altitude. They are particularly useful for identifying high-altitude clouds, such as cirrus clouds, which are often associated with fair weather.
-
Visible Light Cloud Maps: These maps rely on reflected sunlight to visualize cloud cover. They are effective for identifying low-altitude clouds, such as cumulus and stratus clouds, which are often associated with precipitation.
-
Combined Infrared and Visible Light Maps: These maps combine data from both infrared and visible light sensors to provide a comprehensive view of cloud characteristics. They are particularly valuable for understanding the vertical structure of clouds and their potential for producing precipitation.
Benefits of Satellite Cloud Maps:
Satellite cloud maps offer numerous benefits for various applications:
-
Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists use satellite cloud maps to track cloud movement, identify storm systems, and predict weather patterns. This information is crucial for issuing timely and accurate weather forecasts, helping to protect lives and property.
-
Aviation Safety: Pilots rely on satellite cloud maps to navigate safely through airspace, avoiding hazardous weather conditions. These maps provide valuable insights into cloud altitudes, densities, and potential turbulence, enhancing flight safety.
-
Agriculture: Farmers use satellite cloud maps to monitor irrigation needs, assess crop health, and predict potential weather events that could impact their harvests. This information helps optimize agricultural practices and ensure food security.
-
Disaster Preparedness: Satellite cloud maps are instrumental in disaster preparedness efforts. They can identify areas at risk of flooding, landslides, and other weather-related disasters, allowing for early warning systems and evacuation plans.
-
Climate Monitoring: Scientists use satellite cloud maps to track long-term changes in cloud cover and distribution, providing insights into climate change and its impacts on the Earth’s climate system.
FAQs about Satellite Cloud Maps:
Q: How accurate are satellite cloud maps?
The accuracy of satellite cloud maps depends on various factors, including the quality of satellite data, the sophistication of processing algorithms, and the specific cloud properties being measured. While maps provide valuable insights, it’s important to note that they may not always be completely accurate, especially in areas with limited satellite coverage or complex cloud formations.
Q: How often are satellite cloud maps updated?
Satellite cloud maps are typically updated every few hours, depending on the specific satellite system and the level of detail required. Some systems provide near-real-time updates, allowing for continuous monitoring of cloud activity.
Q: What are the limitations of satellite cloud maps?
While satellite cloud maps provide valuable information, they have limitations. For example, they may not be able to accurately depict cloud features in areas with heavy cloud cover or complex atmospheric conditions. Additionally, some sensors may have difficulty distinguishing between clouds and other atmospheric phenomena, such as smoke or dust.
Q: Can I access satellite cloud maps online?
Yes, numerous websites and online platforms offer access to satellite cloud maps. These resources often provide interactive maps, allowing users to zoom in on specific locations, track cloud movement, and explore historical data.
Tips for Using Satellite Cloud Maps:
-
Understand the limitations: Be aware of the potential limitations of satellite cloud maps, including accuracy limitations and the possibility of misinterpreting data.
-
Consider the context: Interpret satellite cloud maps within the context of other meteorological information, such as surface weather observations and numerical weather models.
-
Use reliable sources: Access satellite cloud maps from reputable sources, such as government agencies, meteorological organizations, and established scientific institutions.
-
Explore interactive features: Utilize interactive features offered by online platforms, such as zooming, panning, and time-lapse animations, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of cloud dynamics.
Conclusion:
Satellite cloud maps have revolutionized our understanding of cloud formations, providing valuable insights for a wide range of applications. From weather forecasting and aviation safety to agriculture and disaster preparedness, these tools empower us to better understand and manage the complex interplay between clouds and our planet. As satellite technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and accurate cloud maps, further enhancing our ability to predict, prepare for, and adapt to the dynamic world of clouds.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Satellite Cloud Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!