Unveiling the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Vulnerability Mapping
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Vulnerability Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Vulnerability Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Vulnerability Mapping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Vulnerability Mapping
- 3.1 Defining the Terrain: Understanding Vulnerability Mapping
- 3.2 The Power of Insight: Benefits of Vulnerability Mapping
- 3.3 Navigating the Landscape: Techniques and Tools
- 3.4 Building a Robust Strategy: Key Considerations
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions:
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Vulnerability Mapping:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Vulnerability Mapping
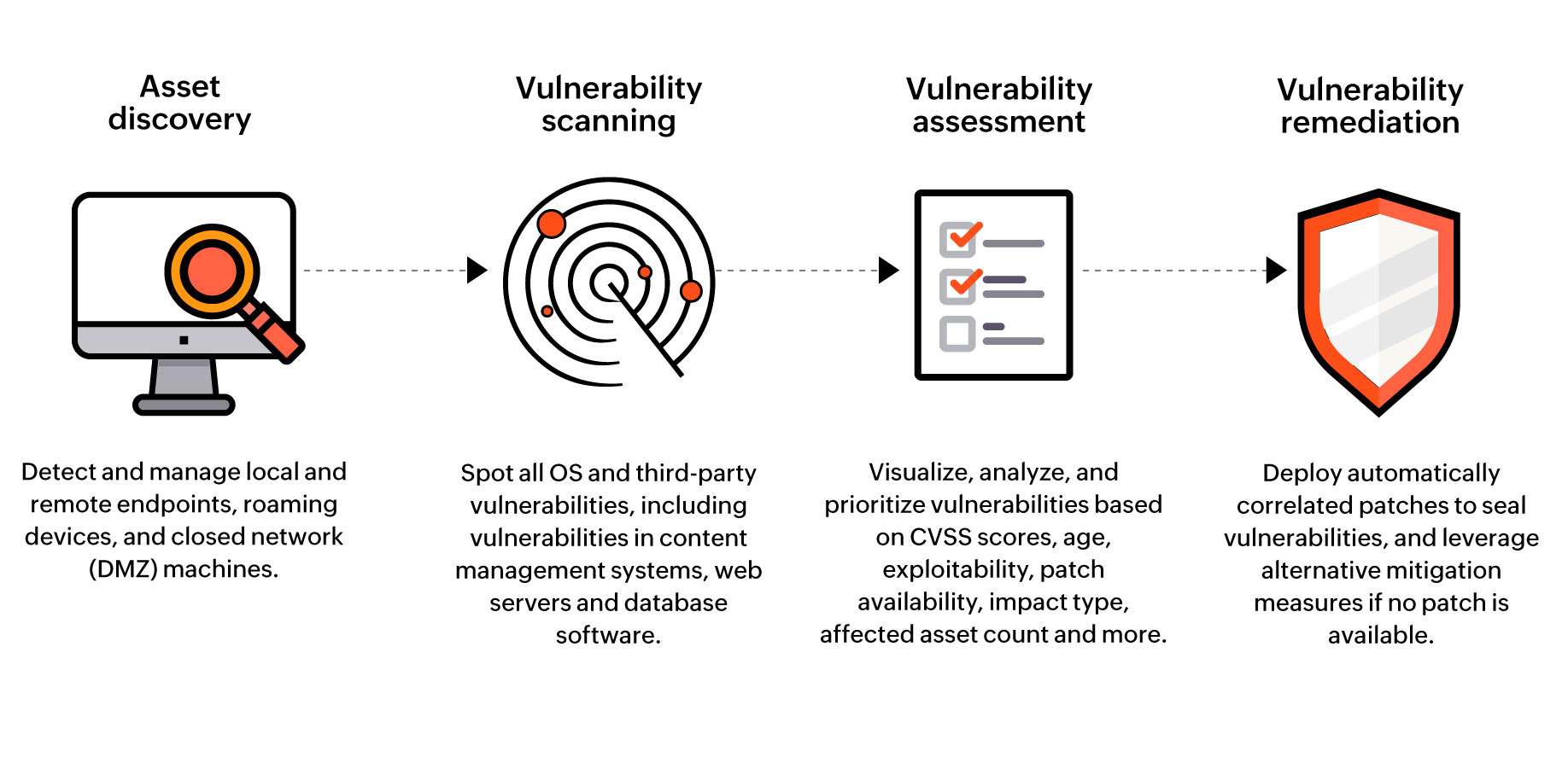
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, organizations face a constant battle to protect their sensitive data and critical infrastructure. Navigating this complex terrain requires a strategic approach, one that involves understanding and addressing vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Enter vulnerability mapping, a powerful tool that empowers organizations to proactively identify, assess, and prioritize potential weaknesses in their systems and networks.
Defining the Terrain: Understanding Vulnerability Mapping
Vulnerability mapping is a systematic process of identifying, documenting, and analyzing potential weaknesses within an organization’s IT infrastructure, applications, and systems. It goes beyond simply listing vulnerabilities; it seeks to understand their potential impact, prioritize remediation efforts, and ultimately strengthen the organization’s overall security posture.
At its core, vulnerability mapping involves:
- Identification: Scanning and analyzing systems and applications to detect known vulnerabilities using various techniques like automated scanners, penetration testing, and manual assessments.
- Documentation: Creating a detailed inventory of identified vulnerabilities, including their severity, exploitability, and potential impact.
- Prioritization: Categorizing vulnerabilities based on their risk level, taking into account factors like likelihood of exploitation, potential damage, and business impact.
- Remediation: Developing and implementing plans to address prioritized vulnerabilities, whether through patching, configuration changes, or other mitigation strategies.
The Power of Insight: Benefits of Vulnerability Mapping
Implementing a robust vulnerability mapping program yields significant benefits, enhancing an organization’s security posture and safeguarding its critical assets.
- Proactive Risk Mitigation: Vulnerability mapping allows organizations to identify potential threats before they are exploited, enabling proactive risk mitigation and preventing costly data breaches, system downtime, and reputational damage.
- Enhanced Security Awareness: The process of vulnerability mapping fosters a culture of security awareness within the organization, encouraging staff to prioritize security best practices and report potential vulnerabilities.
- Improved Compliance: Many regulatory frameworks, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR, require organizations to demonstrate their commitment to security and vulnerability management. Vulnerability mapping provides the necessary documentation and evidence to meet these compliance requirements.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: By prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their risk level, organizations can allocate resources effectively, focusing on the most critical threats and maximizing their security investments.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Vulnerability mapping provides valuable data and insights that inform security decisions, enabling organizations to make informed choices regarding investments in security tools, training, and policies.
Navigating the Landscape: Techniques and Tools
The effectiveness of vulnerability mapping hinges on the chosen techniques and tools. Organizations can leverage a range of methods to identify and analyze vulnerabilities, each with its own strengths and limitations:
- Automated Vulnerability Scanners: These tools use pre-defined rules and databases to identify known vulnerabilities in systems and applications. While efficient for large-scale scans, they may miss custom-built applications or vulnerabilities not yet documented in databases.
- Penetration Testing: Ethical hackers simulate real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities and assess the organization’s security defenses. This hands-on approach provides a realistic assessment of security weaknesses but can be resource-intensive.
- Manual Assessments: Security experts conduct manual reviews of systems, configurations, and code to identify vulnerabilities. This method is highly effective for uncovering complex or custom-built vulnerabilities but can be time-consuming.
- Vulnerability Management Platforms: These platforms integrate various tools and techniques, providing a centralized dashboard for managing vulnerabilities, tracking remediation progress, and reporting on security posture.
Building a Robust Strategy: Key Considerations
Implementing a successful vulnerability mapping program requires careful planning and consideration of various factors:
- Scope and Focus: Determine the scope of the mapping exercise, considering the criticality of systems, potential impact of vulnerabilities, and compliance requirements.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Establish a robust process for collecting data from various sources, including system logs, security audits, and vulnerability scans.
- Prioritization and Remediation: Develop a clear framework for prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their severity, exploitability, and business impact.
- Communication and Reporting: Establish effective communication channels to keep stakeholders informed about identified vulnerabilities, remediation plans, and overall security posture.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Implement ongoing monitoring and assessment to identify new vulnerabilities, track remediation progress, and adapt the vulnerability mapping program to evolving threats.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the different types of vulnerabilities?
A: Vulnerabilities can be classified based on their nature and the potential impact they pose. Common types include:
- Operating System Vulnerabilities: Weaknesses in the core operating system, such as buffer overflows, privilege escalation, and denial-of-service vulnerabilities.
- Application Vulnerabilities: Security flaws in software applications, such as cross-site scripting (XSS), SQL injection, and authentication bypass vulnerabilities.
- Network Vulnerabilities: Weaknesses in network infrastructure, such as misconfigured firewalls, weak password policies, and open ports.
- Physical Security Vulnerabilities: Weaknesses in physical security measures, such as inadequate access control, lack of surveillance, and vulnerable data storage.
Q: How often should vulnerability mapping be performed?
A: The frequency of vulnerability mapping depends on factors such as the organization’s risk tolerance, the complexity of its IT infrastructure, and the rate of change in its technology environment. Generally, vulnerability mapping should be conducted at least annually, with more frequent scans for critical systems or in the event of significant changes to the IT environment.
Q: Who is responsible for vulnerability mapping?
A: The responsibility for vulnerability mapping often falls on a dedicated security team or a designated individual. However, the process requires collaboration across different departments, including IT, operations, and legal.
Q: What are the challenges associated with vulnerability mapping?
A: Vulnerability mapping can present several challenges, including:
- Resource Constraints: The process can be resource-intensive, requiring specialized tools, skilled personnel, and dedicated time.
- False Positives: Automated scanners may generate false positives, requiring manual verification and potentially wasting valuable time.
- Keeping Up with Emerging Threats: The rapidly evolving threat landscape requires ongoing monitoring and updates to vulnerability databases and security tools.
- Integrating with Other Security Processes: Vulnerability mapping should be integrated with other security processes, such as incident response and security awareness training.
Tips for Effective Vulnerability Mapping:
- Start with a Clear Scope: Define the scope of the mapping exercise, focusing on critical systems and applications.
- Utilize a Multi-Layered Approach: Combine automated scanning, penetration testing, and manual assessments to achieve comprehensive coverage.
- Prioritize Based on Risk: Categorize vulnerabilities based on their severity, exploitability, and potential impact to prioritize remediation efforts.
- Automate Where Possible: Utilize tools and platforms to automate repetitive tasks, freeing up time for more strategic activities.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of emerging threats and vulnerabilities by subscribing to security advisories and attending industry events.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Involve relevant stakeholders, such as IT, operations, and legal, in the vulnerability mapping process.
Conclusion:
Vulnerability mapping is an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to strengthen their security posture and protect their valuable assets in the face of evolving cyber threats. By proactively identifying, assessing, and prioritizing vulnerabilities, organizations can mitigate risks, optimize resource allocation, and ensure ongoing compliance with security standards. Implementing a robust vulnerability mapping program empowers organizations to navigate the complex digital landscape with confidence, safeguarding their critical data and infrastructure from the ever-present threat of cyberattacks.

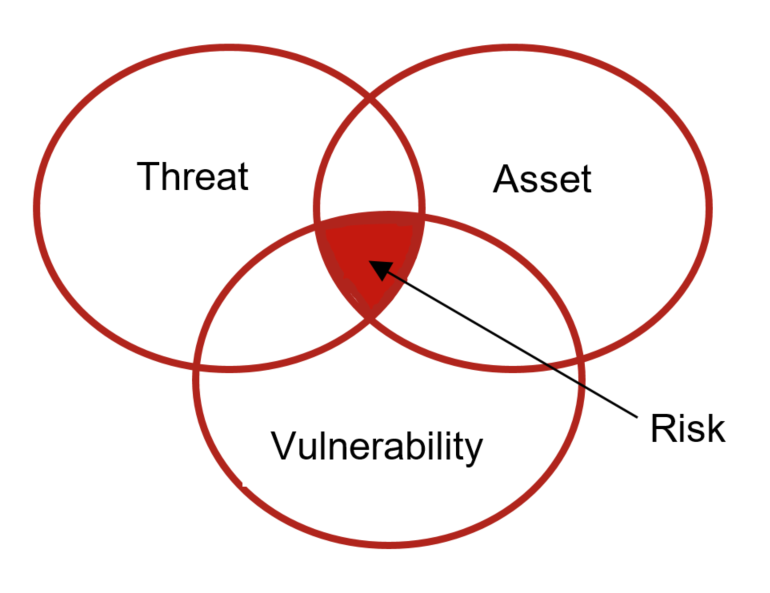
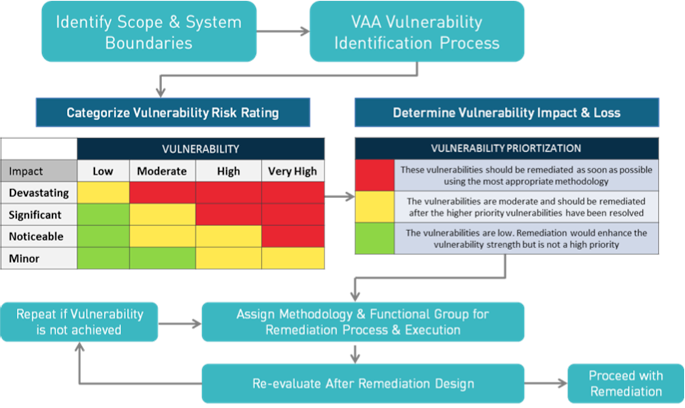



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Vulnerability Mapping. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!