Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Mexico: A Journey Through its Topography
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Mexico: A Journey Through its Topography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Mexico: A Journey Through its Topography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Mexico: A Journey Through its Topography

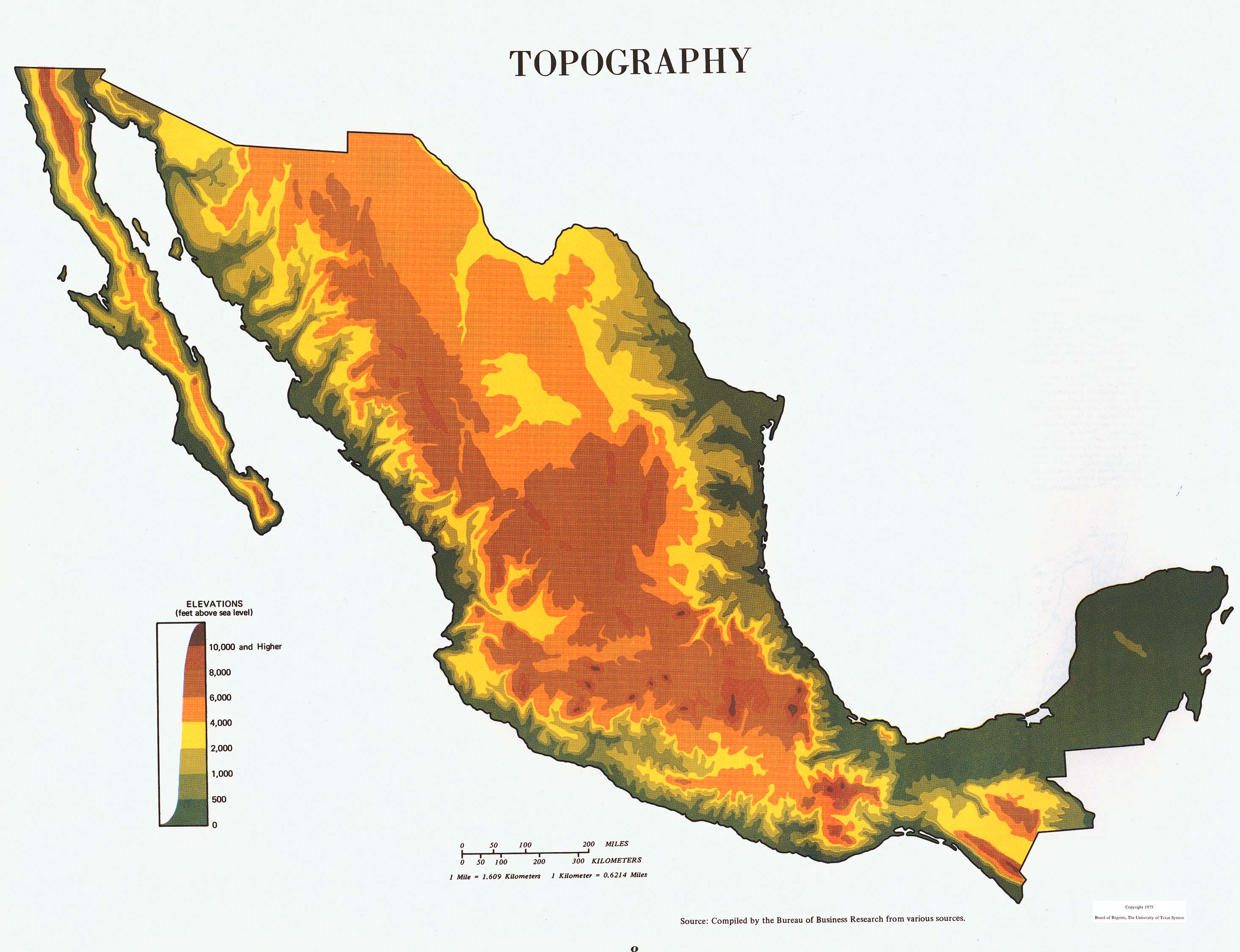
Mexico, a vibrant nation nestled between North and Central America, boasts a captivating landscape shaped by a rich geological history. Its topography, a tapestry woven with towering mountains, fertile valleys, arid deserts, and sprawling coastal plains, plays a vital role in shaping the country’s diverse ecosystems, cultural heritage, and economic activities. Understanding Mexico’s topography is crucial for comprehending its natural beauty, its challenges, and its potential.
A Tapestry of Landforms:
Mexico’s topography is a captivating mosaic of contrasting landforms, each contributing to the country’s unique character.
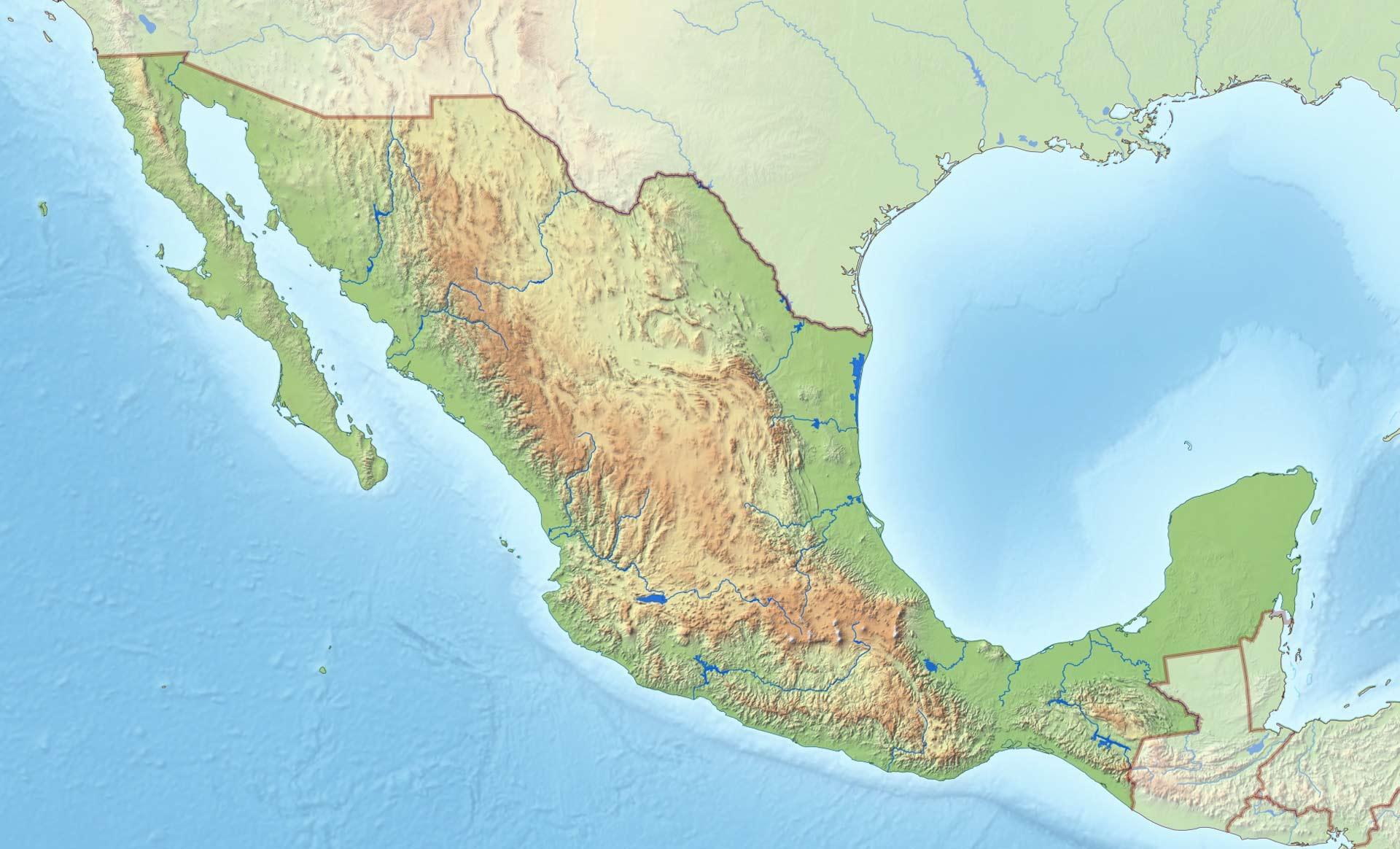
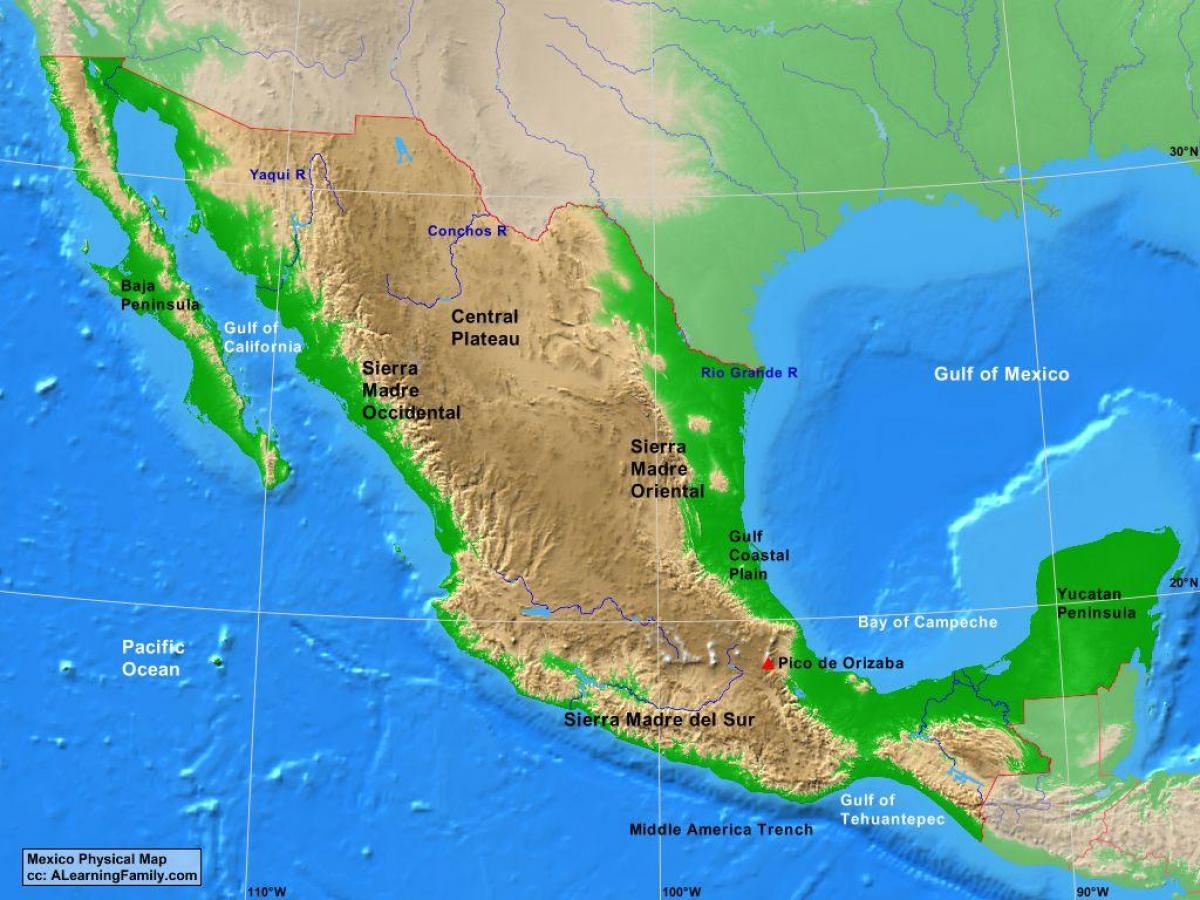
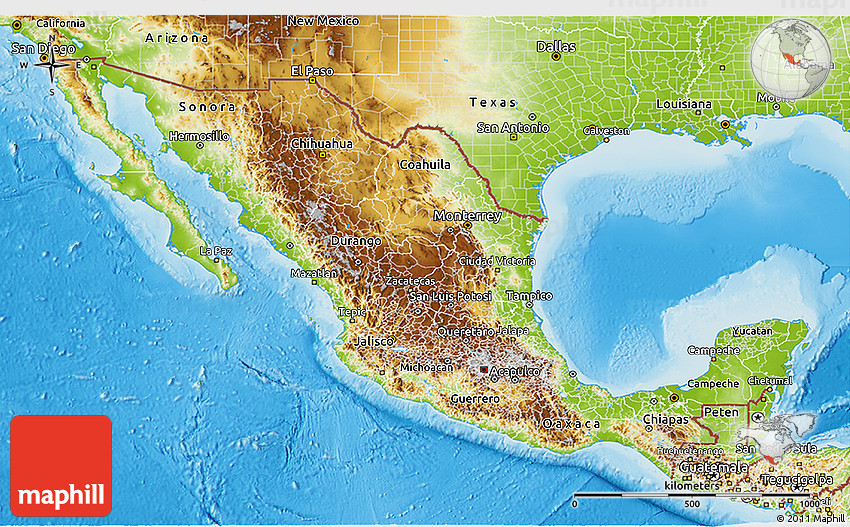
1. The Mighty Sierra Madre:
Dominating much of Mexico’s interior, the Sierra Madre mountain ranges form a backbone, stretching from north to south. This majestic mountain system comprises three distinct chains:
- Sierra Madre Occidental: Rising in the northwest, this range is characterized by its rugged, volcanic peaks, deep canyons, and lush forests.
- Sierra Madre Oriental: Extending along the eastern side of the Mexican Plateau, this range is known for its steep slopes, limestone formations, and dramatic canyons.
- Sierra Madre del Sur: Located in southern Mexico, this range features lower elevations, abundant rainfall, and a mix of forested hills and coastal plains.
2. The Mexican Plateau:
Nestled between the Sierra Madre Occidental and Oriental, the Mexican Plateau is a vast, elevated region encompassing much of central Mexico. This plateau is characterized by its arid climate, rolling hills, and fertile valleys, making it ideal for agriculture.
3. The Coastal Plains:
Bordering the Pacific Ocean in the west and the Gulf of Mexico in the east, Mexico’s coastal plains offer a stark contrast to the mountainous interior. These low-lying areas are characterized by their diverse ecosystems, ranging from sandy beaches and mangrove swamps to lush rainforests and fertile farmlands.
4. The Baja California Peninsula:
Stretching south from the U.S. border, the Baja California Peninsula is a unique geological feature, characterized by its arid desert landscapes, volcanic formations, and rugged mountain ranges.
5. The Yucatán Peninsula:
Located in southeastern Mexico, the Yucatán Peninsula is a flat, limestone plateau known for its dense jungle, cenotes (natural sinkholes), and ancient Mayan ruins.
The Influence of Topography on Mexico’s Ecosystem:
Mexico’s diverse topography plays a crucial role in shaping its diverse ecosystems. The varied elevations, rainfall patterns, and soil types create a mosaic of habitats, each supporting a unique array of plant and animal life.
1. Biodiversity Hotspots:
Mexico is considered one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots, with a wide range of ecosystems, including rainforests, deserts, grasslands, and wetlands. The Sierra Madre Occidental and Oriental, with their diverse elevations and microclimates, support a rich tapestry of plant and animal life.
2. Unique Flora and Fauna:
Mexico’s diverse topography is home to a remarkable array of flora and fauna, including endemic species found nowhere else in the world. The desert landscapes of Baja California and the Yucatán Peninsula support unique cacti and reptiles, while the rainforests of Chiapas and Veracruz are home to a multitude of colorful birds, mammals, and insects.
3. Natural Resources:
Mexico’s topography also plays a vital role in shaping its natural resources. The mountains are rich in minerals, including silver, gold, and copper, while the coastal plains offer fertile farmland and abundant fisheries.
The Impact of Topography on Mexican Culture and Society:
Mexico’s topography has profoundly influenced its cultural heritage and societal development.
1. Regional Diversity:
The varied landscape has led to the development of distinct regional cultures and traditions. The mountainous regions are often home to indigenous communities with unique languages, customs, and artistic expressions, while the coastal areas have been shaped by maritime traditions and the influence of other cultures.
2. Transportation and Infrastructure:
Mexico’s mountainous terrain poses significant challenges for transportation and infrastructure development. Constructing roads, railways, and other infrastructure projects in mountainous regions can be expensive and difficult.
3. Agriculture and Economic Development:
Mexico’s topography plays a crucial role in its agricultural production. The fertile valleys of the Mexican Plateau are ideal for growing crops like corn, beans, and wheat, while the coastal plains are suited for cultivating fruits, vegetables, and livestock.
FAQs about the Topography of Mexico:
1. What is the highest mountain in Mexico?
The highest mountain in Mexico is Pico de Orizaba, also known as Citlaltépetl, with an elevation of 5,636 meters (18,491 feet).
2. What are the main geographical regions of Mexico?
The main geographical regions of Mexico are the Sierra Madre mountain ranges, the Mexican Plateau, the coastal plains, the Baja California Peninsula, and the Yucatán Peninsula.
3. What are some of the major rivers in Mexico?
Some of the major rivers in Mexico include the Rio Grande, the Colorado River, the Balsas River, and the Grijalva River.
4. How does the topography of Mexico affect its climate?
Mexico’s topography plays a significant role in shaping its climate. The mountains create rain shadows, leading to arid conditions in the interior, while the coastal plains experience a more humid climate.
5. What are some of the environmental challenges facing Mexico due to its topography?
Mexico faces a range of environmental challenges due to its topography, including deforestation, soil erosion, water scarcity, and the vulnerability of coastal areas to natural disasters.
Tips for Exploring Mexico’s Topography:
1. Hiking and Trekking:
Mexico offers a wide range of hiking and trekking opportunities, from challenging climbs in the Sierra Madre to scenic trails in the coastal plains.
2. Road Trips:
Embark on a scenic road trip to explore Mexico’s diverse landscape, from the volcanic landscapes of the Sierra Madre Occidental to the arid beauty of Baja California.
3. Kayaking and Canoeing:
Explore the waterways of Mexico by kayak or canoe, navigating through mangrove swamps, cenotes, and rivers.
4. Visit National Parks:
Mexico boasts a network of national parks that protect its diverse ecosystems, offering opportunities for wildlife viewing, hiking, and camping.
Conclusion:
Mexico’s topography is a captivating tapestry of contrasting landforms, shaping its diverse ecosystems, cultural heritage, and economic activities. From the towering peaks of the Sierra Madre to the fertile valleys of the Mexican Plateau, understanding Mexico’s topography is essential for appreciating its natural beauty, its challenges, and its potential. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate connections between Mexico’s land and its people, we gain a deeper understanding of this vibrant nation’s unique character.



_1.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Mexico: A Journey Through its Topography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!