Unveiling New Mexico’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Relief Map
Related Articles: Unveiling New Mexico’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Relief Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling New Mexico’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Relief Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling New Mexico’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Relief Map
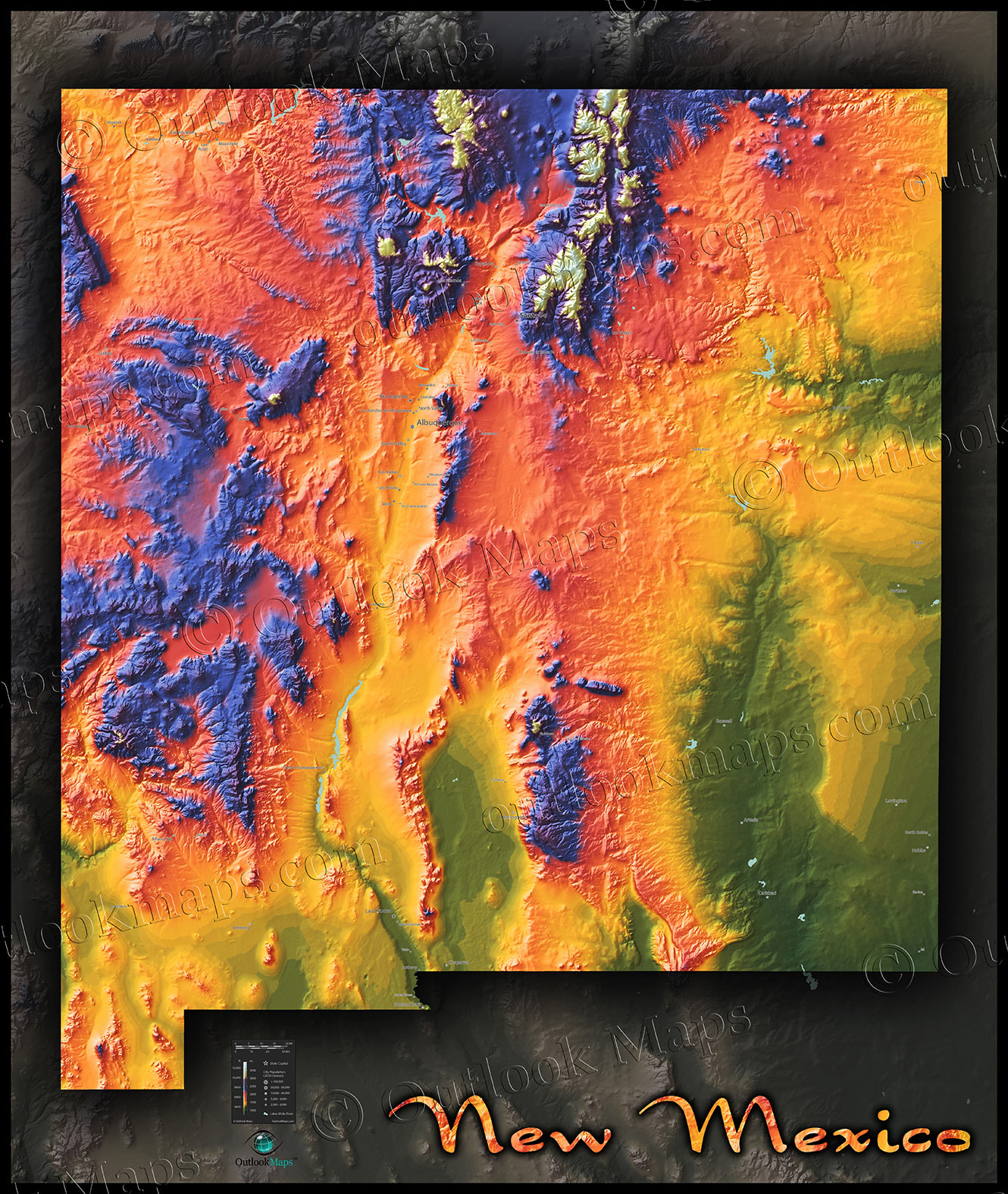
New Mexico, a state in the southwestern United States, boasts a captivating landscape that is as diverse as it is stunning. From towering mountain ranges to vast deserts and sprawling plains, the state’s relief map tells a story of geological forces shaping a unique and captivating environment. Understanding the relief map of New Mexico is crucial for appreciating its natural beauty, comprehending its ecological diversity, and appreciating the challenges and opportunities presented by its terrain.
Understanding the Relief Map
A relief map, also known as a topographic map, depicts the elevation and shape of the Earth’s surface. It uses contour lines to represent points of equal elevation, creating a visual representation of the land’s undulations and slopes. The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the terrain.
The Key Features of New Mexico’s Relief Map
New Mexico’s relief map is characterized by several prominent features that contribute to its unique geography:
- The Rocky Mountains: The state’s western border is defined by the Sangre de Cristo Mountains, a subrange of the Rocky Mountains. These mountains reach elevations exceeding 13,000 feet, offering breathtaking views and opportunities for outdoor recreation.
- The Rio Grande Rift: This geological feature runs through the center of New Mexico, creating a valley that is home to the Rio Grande River and several smaller rivers. The rift is characterized by its relatively flat terrain and its distinctive volcanic landscape.
- The Basin and Range Province: This region, covering much of western and central New Mexico, is characterized by alternating ranges of mountains and valleys. The ranges are often formed by volcanic activity and uplift, while the valleys are filled with sediment eroded from the mountains.
- The Colorado Plateau: The northeastern portion of New Mexico is part of the Colorado Plateau, a vast, high-elevation region known for its canyons, mesas, and buttes. The iconic Chaco Culture National Historical Park, with its ancient Puebloan ruins, lies within this region.
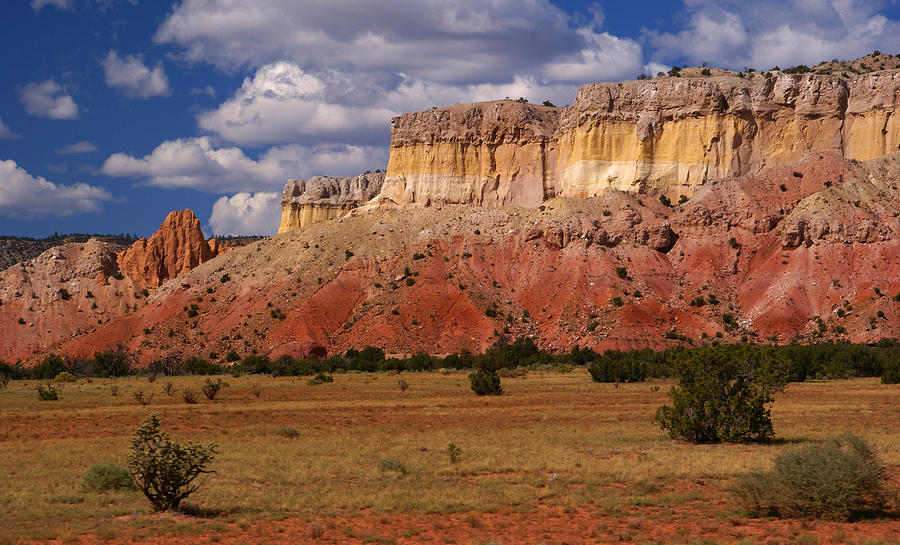
- The Chihuahuan Desert: This vast desert occupies much of southern New Mexico, characterized by its arid climate, sparse vegetation, and striking rock formations. The White Sands National Park, with its gypsum dunes, is a prominent feature of this region.
The Importance of New Mexico’s Relief Map
The relief map of New Mexico is significant for several reasons:
- Ecological Diversity: The varied terrain of New Mexico supports a wide array of ecosystems, ranging from high-altitude alpine meadows to arid deserts. This diversity is reflected in the state’s flora and fauna, making it a haven for wildlife and a hotspot for biodiversity.
- Water Resources: The relief map plays a crucial role in shaping the state’s water resources. The mountains serve as watersheds, providing sources of water for rivers, lakes, and aquifers. The distribution of these water resources is influenced by the topography, with some areas experiencing abundant rainfall and others facing chronic drought.
- Economic Development: The relief map influences the state’s economic activities. The mountains provide opportunities for mining, forestry, and tourism. The valleys offer fertile land for agriculture, while the deserts hold potential for renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
- Infrastructure Development: The challenging terrain of New Mexico presents significant obstacles for infrastructure development. Roads, railways, and pipelines need to be carefully planned and constructed to navigate the mountains, canyons, and deserts.
- Cultural Heritage: The relief map has shaped the cultural heritage of New Mexico. The state’s indigenous populations have adapted to the diverse terrain, developing unique traditions and ways of life. The state’s history is interwoven with the landscape, from the ancient Puebloan settlements to the modern-day ranching and farming communities.
Exploring the Relief Map: A Deeper Dive
To gain a deeper understanding of New Mexico’s relief map, it’s essential to explore its key features in more detail:
The Rocky Mountains:
- Elevation: The Sangre de Cristo Mountains, a subrange of the Rocky Mountains, are the highest in New Mexico, reaching elevations exceeding 13,000 feet.
- Geological Formation: These mountains were formed by tectonic uplift, with granite and metamorphic rocks exposed at the surface.
- Ecological Importance: The mountains support a variety of ecosystems, including high-elevation forests, alpine meadows, and rocky slopes. They are home to a diverse array of wildlife, including elk, deer, bears, and mountain lions.
The Rio Grande Rift:
- Geological Significance: The Rio Grande Rift is a major geological feature that extends from Colorado to Texas. It is a zone of crustal stretching and thinning, resulting in volcanic activity and the formation of a valley.
- River System: The Rio Grande River flows through the rift, providing a vital source of water for agriculture and communities.
- Volcanic Landscape: The rift is characterized by volcanic features, including lava flows, cinder cones, and calderas. The Valles Caldera National Preserve, a volcanic caldera, is a prominent feature of the rift.
The Basin and Range Province:
- Geological Formation: The Basin and Range Province is characterized by alternating ranges of mountains and valleys. These features are formed by tectonic forces that cause the crust to stretch and break, creating a series of fault blocks.
- Arid Climate: The Basin and Range Province experiences an arid climate, with sparse vegetation and limited water resources.
- Unique Landscape: The region is known for its rugged terrain, including jagged mountain peaks, deep canyons, and dry washes.
The Colorado Plateau:
- High Elevation: The Colorado Plateau is a vast, high-elevation region characterized by its flat-lying sedimentary rocks.
- Canyon Formation: The region is home to iconic canyons, including the Grand Canyon, which is partially located in northern Arizona.
- Ancient Ruins: The Chaco Culture National Historical Park, located in the northwestern part of the Colorado Plateau, is home to ancient Puebloan ruins that date back to the 12th century.
The Chihuahuan Desert:
- Aridity: The Chihuahuan Desert is one of the largest deserts in North America, characterized by its extreme aridity and sparse vegetation.
- Unique Features: The desert is known for its striking rock formations, including gypsum dunes at White Sands National Park and volcanic peaks in the Organ Mountains.
- Adaptation: The desert’s harsh conditions have shaped the flora and fauna, with many species exhibiting remarkable adaptations to survive the lack of water and extreme temperatures.
FAQs about New Mexico’s Relief Map
Q: What is the highest point in New Mexico?
A: The highest point in New Mexico is Wheeler Peak, located in the Sangre de Cristo Mountains, at an elevation of 13,161 feet.
Q: What is the lowest point in New Mexico?
A: The lowest point in New Mexico is the Red Bluff, located on the Pecos River, at an elevation of 2,817 feet.
Q: What are the major rivers in New Mexico?
A: The major rivers in New Mexico include the Rio Grande, the Pecos River, the San Juan River, and the Canadian River.
Q: What are the major cities in New Mexico?
A: The major cities in New Mexico include Albuquerque, Santa Fe, Las Cruces, and Roswell.
Q: What are the main economic activities in New Mexico?
A: The main economic activities in New Mexico include tourism, agriculture, mining, oil and gas production, and government services.
Q: What are the major natural resources in New Mexico?
A: The major natural resources in New Mexico include oil, natural gas, coal, potash, copper, and timber.
Q: What are the major environmental challenges facing New Mexico?
A: The major environmental challenges facing New Mexico include water scarcity, desertification, air pollution, and climate change.
Tips for Understanding New Mexico’s Relief Map
- Use a topographic map: Topographic maps provide detailed information about elevation and terrain, making it easier to visualize the landscape.
- Visit New Mexico: Experiencing the state’s diverse terrain firsthand will provide a deeper understanding of its relief map.
- Learn about the state’s geology: Understanding the geological forces that shaped New Mexico’s landscape will provide valuable context for interpreting the relief map.
- Explore the state’s natural parks: New Mexico’s national parks and state parks offer opportunities to explore its diverse ecosystems and appreciate the beauty of its relief map.
- Read about the state’s history and culture: The history and culture of New Mexico are intertwined with its landscape, providing a richer understanding of the state’s relief map.
Conclusion
New Mexico’s relief map is a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped its diverse and captivating landscape. Understanding this map is crucial for appreciating the state’s natural beauty, comprehending its ecological diversity, and recognizing the challenges and opportunities presented by its terrain. Whether you are a hiker, a geologist, or simply someone who appreciates the beauty of the natural world, exploring the relief map of New Mexico will reveal a fascinating story of geological history and ecological wonder.


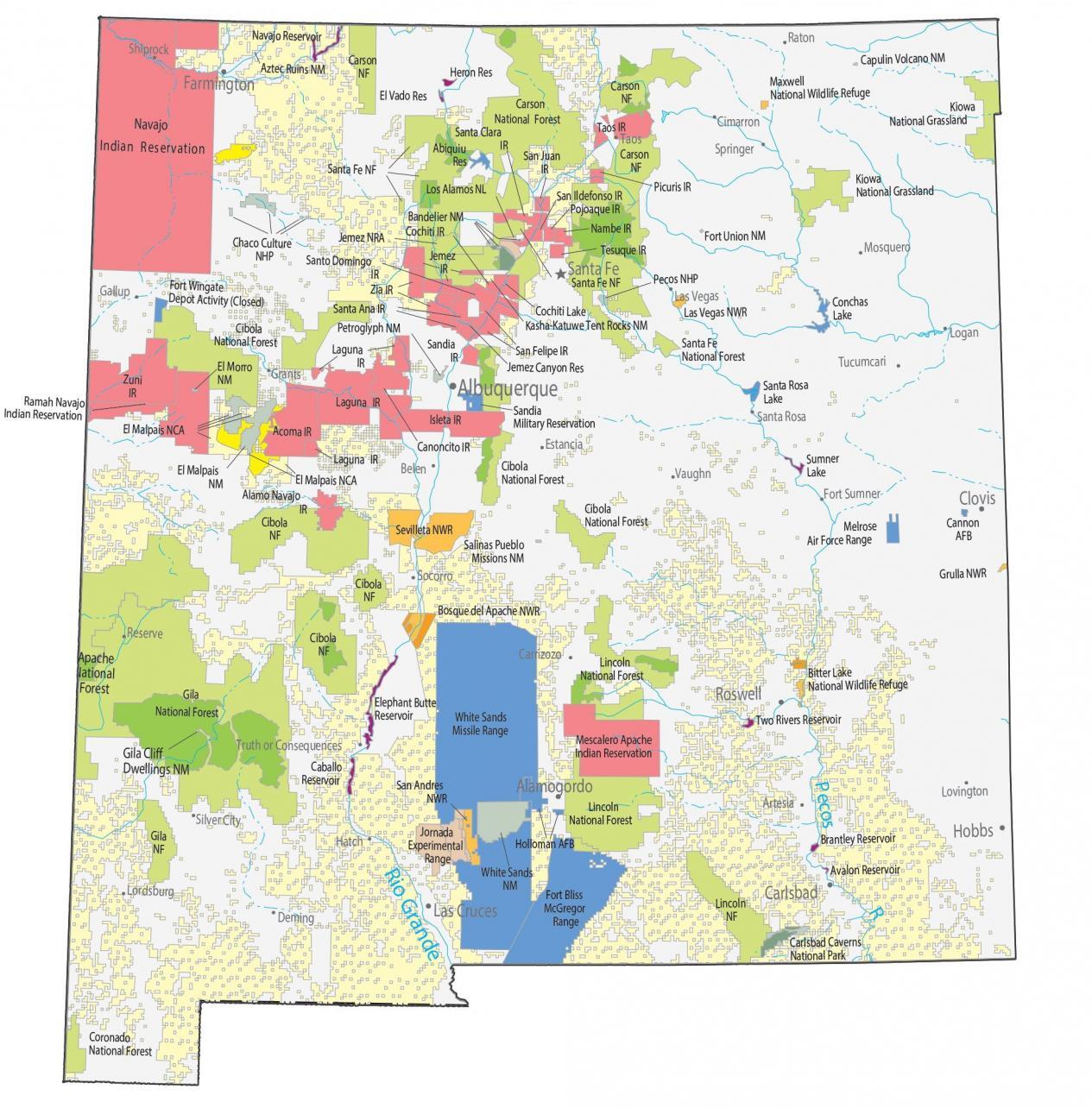




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling New Mexico’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Relief Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!