Unraveling the Tapestry of Rome: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Rome: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Rome: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Rome: A Geographical Exploration

Rome, the Eternal City, is a captivating blend of history, culture, and natural beauty. Its geographical tapestry, a mosaic of rolling hills, fertile plains, and ancient river valleys, has played a pivotal role in shaping its destiny. Understanding the geography of Rome is essential for appreciating its historical significance, its urban development, and its enduring appeal.
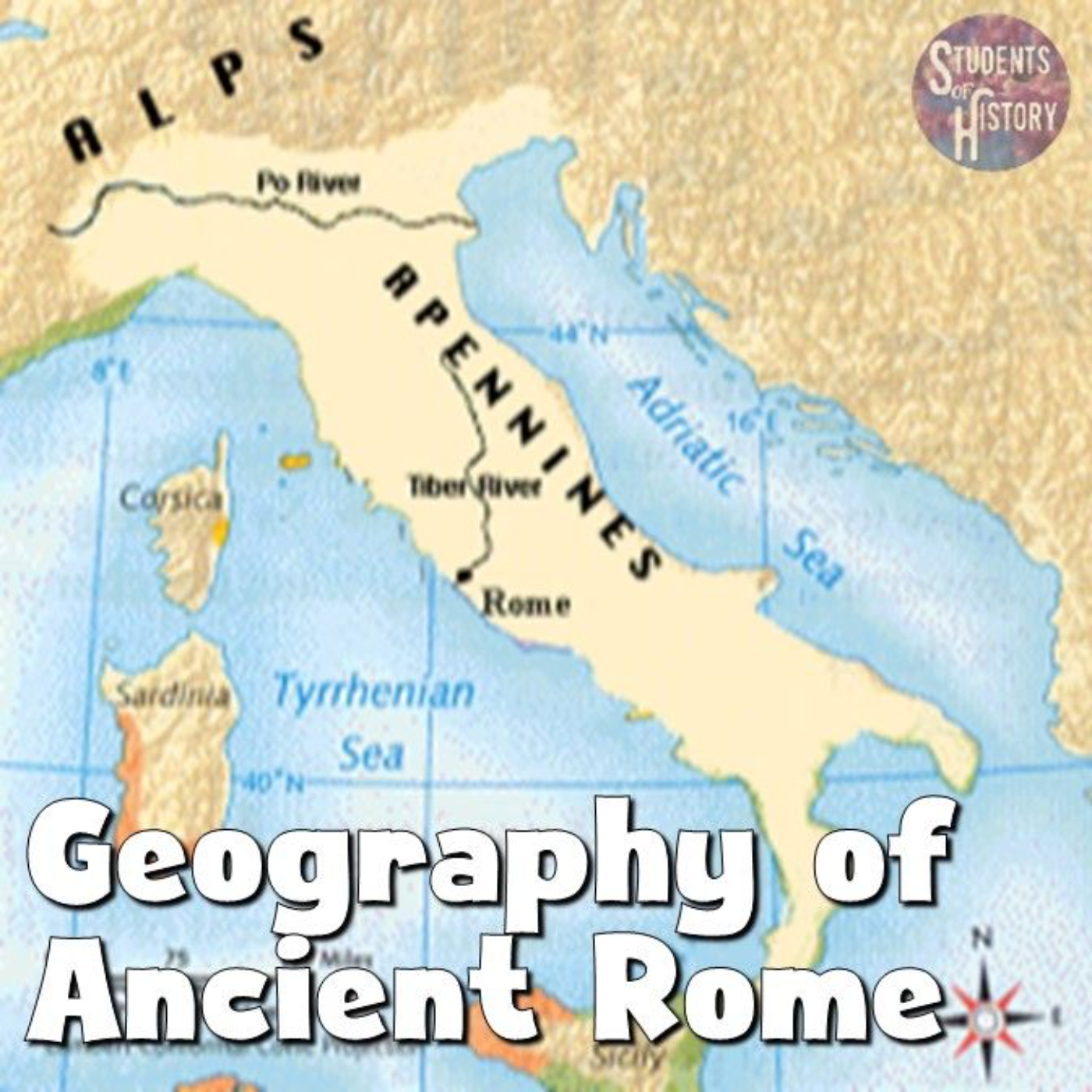
The Lay of the Land: A Geographical Overview
Rome is situated in the heart of the Lazio region of central Italy, nestled on the banks of the Tiber River. The city occupies a strategic position on the western edge of the Italian Peninsula, where the Apennine Mountains meet the coastal plains. This geographical location has historically facilitated trade and communication, contributing to Rome’s rise as a major power.
The Tiber River: A Lifeline and a Defining Feature
The Tiber River, a vital artery that cuts through the city, has played a crucial role in Rome’s history. Its fertile banks provided sustenance and facilitated the development of agriculture. The river served as a vital waterway for transportation, trade, and defense, connecting Rome to the sea and the surrounding regions. The Tiber’s confluence with the Aniene River, which flows through the city’s northeastern outskirts, further enhanced its strategic importance.
The Seven Hills of Rome: A Legacy of Ancient Planning
Rome’s iconic seven hills, each with its own unique character and historical significance, are a defining feature of the city’s landscape. These hills, namely the Palatine, Aventine, Capitoline, Quirinal, Viminal, Esquiline, and Caelian, were strategically chosen for their defensive positions and access to resources. The ancient Romans built their city around these hills, utilizing their natural contours for urban planning and development.
The Roman Campagna: A Fertile Plain and a Historical Tapestry
The Roman Campagna, a sprawling plain surrounding Rome, was once a fertile agricultural region that provided sustenance for the city. Its rich soil supported vast vineyards, olive groves, and pastures, making it a vital resource for the Roman Empire. Today, the Campagna is a historical landscape dotted with ancient ruins, remnants of the Roman Empire’s grandeur.
The Apennine Mountains: A Majestic Backdrop and a Source of Resources
The Apennine Mountains, a dominant feature of the Italian landscape, provide a majestic backdrop to Rome. These mountains, with their forested slopes and mineral deposits, have historically been a source of resources and inspiration. The mountains served as a natural barrier, protecting Rome from invaders, while also providing access to timber, water, and other essential resources.
The Coastal Plain: A Gateway to the Mediterranean
Rome’s proximity to the Tyrrhenian Sea, a part of the Mediterranean Sea, has been a crucial factor in its history and development. The coastal plain, stretching westward from the city, provided access to trade routes and facilitated the flow of goods and ideas. The sea has also been a source of inspiration for Roman art and literature, shaping the city’s cultural identity.
The Importance of Rome’s Geography
Rome’s geography has played a pivotal role in shaping its history, culture, and urban development. Its strategic location on the Tiber River, its seven hills, its fertile plains, and its proximity to the sea have all contributed to its rise as a major power and its enduring appeal as a cultural center.
Understanding Rome’s Geography: Benefits and Applications
Understanding the geography of Rome offers numerous benefits:
- Historical Perspective: It allows for a deeper appreciation of Rome’s history and the factors that contributed to its rise and fall.
- Urban Planning: The city’s geographical features have influenced its urban development, providing insights into its layout and growth patterns.
- Cultural Understanding: The landscape has shaped Roman art, literature, and mythology, offering a glimpse into the city’s cultural heritage.
- Tourism and Travel: It enhances the experience of visiting Rome, allowing travelers to appreciate the city’s natural beauty and historical significance.
- Environmental Awareness: It highlights the importance of preserving Rome’s natural environment and its role in shaping the city’s identity.
FAQs about Rome’s Geography
Q: What are the seven hills of Rome?
A: The seven hills of Rome are the Palatine, Aventine, Capitoline, Quirinal, Viminal, Esquiline, and Caelian.
Q: What is the significance of the Tiber River to Rome?
A: The Tiber River has been a vital artery for transportation, trade, and defense, connecting Rome to the sea and the surrounding regions.
Q: What is the Roman Campagna?
A: The Roman Campagna is a sprawling plain surrounding Rome, once a fertile agricultural region.
Q: How has Rome’s geography influenced its urban development?
A: Rome’s seven hills, the Tiber River, and the surrounding plains have all played a role in shaping the city’s layout and growth patterns.
Q: What are some of the benefits of understanding Rome’s geography?
A: Understanding Rome’s geography provides historical perspective, enhances tourism experiences, and promotes environmental awareness.
Tips for Exploring Rome’s Geography
- Take a guided tour: A guided tour can provide insights into the city’s history, culture, and geography.
- Visit the Roman Forum and Palatine Hill: These ancient sites offer a glimpse into the city’s origins and urban development.
- Explore the Tiber River: Take a boat tour or walk along the riverbanks to appreciate its role in Rome’s history.
- Visit the Roman Campagna: Explore the surrounding countryside to see remnants of the Roman Empire and experience the natural beauty of the region.
- Learn about the Apennine Mountains: Research their influence on Rome’s history, resources, and culture.
Conclusion
Rome’s geography is an integral part of its identity, shaping its history, culture, and urban development. The Tiber River, the seven hills, the Roman Campagna, the Apennine Mountains, and the coastal plain have all played crucial roles in making Rome the captivating city it is today. By understanding the city’s geographical tapestry, we gain a deeper appreciation for its historical significance, its urban planning, and its enduring appeal.

![The Roman Empire by National Geographic [4961×3152] : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/m0ukNwLpo8cc8NrRwVHgGFoxJWHqWDJ22-_TaLtSYYY.jpg?auto=webpu0026s=6bf19533b9c6791e6f4a2400edd44db4e1531b02)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Rome: A Geographical Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
