Unraveling the Past: A Comprehensive Look at the Tanganyika Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Past: A Comprehensive Look at the Tanganyika Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Past: A Comprehensive Look at the Tanganyika Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Past: A Comprehensive Look at the Tanganyika Map
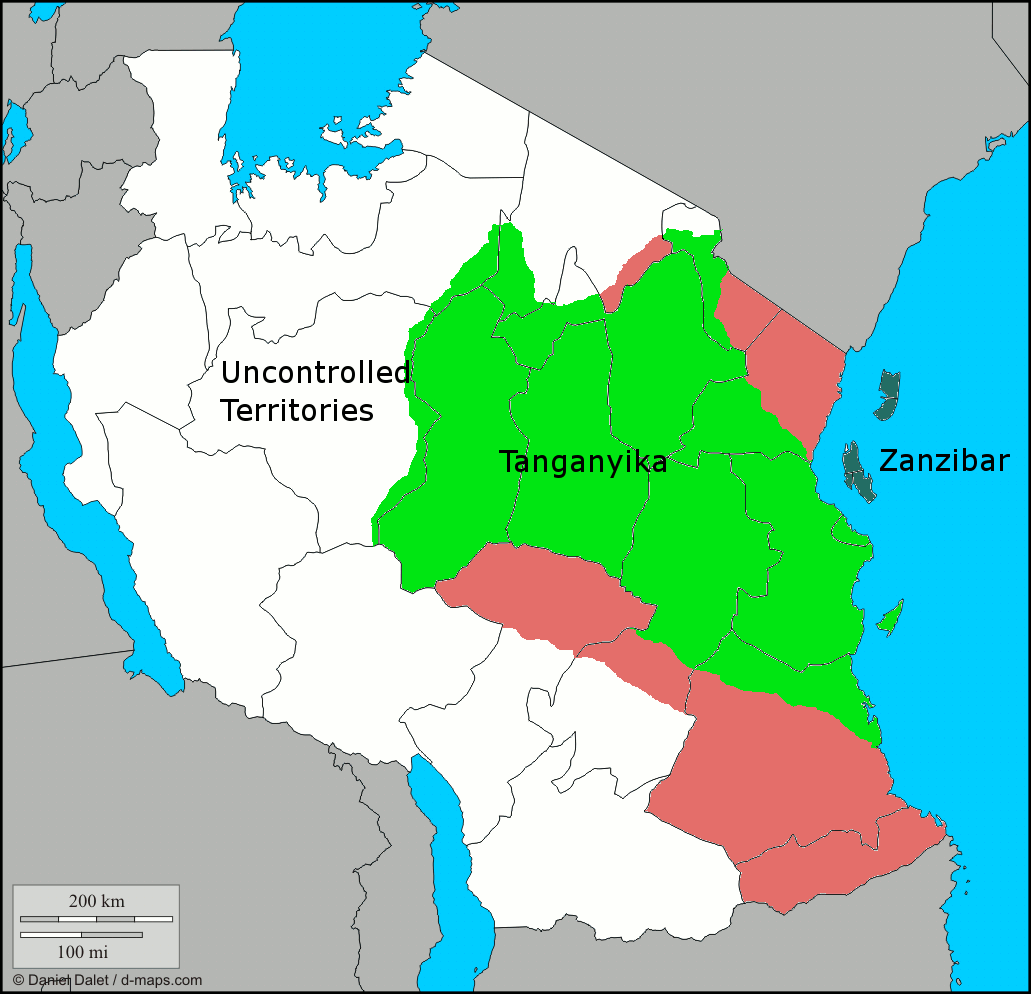
The Tanganyika map, a relic of a bygone era, holds a unique place in the annals of history. It represents a pivotal moment in the formation of modern-day Tanzania, a nation with a rich and complex past. This article delves into the historical context of the Tanganyika map, explores its significance in shaping the political landscape of the region, and illuminates its enduring relevance in understanding the present.
A Glimpse into the Past: The Rise and Fall of Tanganyika
Tanganyika, a vast territory encompassing the eastern portion of present-day Tanzania, experienced a tumultuous journey through the 20th century. Its history is intertwined with the rise and fall of colonial empires, the struggles for independence, and the eventual formation of a unified nation.
The German Era (1884-1919): The story of Tanganyika begins with German colonization. In 1884, German East Africa was established, encompassing Tanganyika, Rwanda, Burundi, and parts of present-day Kenya and Uganda. The German administration, focused on extracting resources and establishing control, left a lasting impact on the region’s infrastructure and social fabric.
British Mandate (1919-1961): Following World War I, Germany lost its colonial possessions, and Tanganyika became a British mandate under the League of Nations. The British period saw the introduction of indirect rule, with local chiefs and leaders serving as intermediaries between the colonial administration and the populace. This period witnessed the development of education, healthcare, and infrastructure, but it also saw the continuation of exploitative practices and the suppression of nationalist movements.
The Struggle for Independence: The seeds of independence were sown in the 1950s, fueled by the growing tide of anti-colonial sentiment across Africa. The Tanganyika African National Union (TANU), led by Julius Nyerere, emerged as the dominant political force, advocating for self-governance. In 1961, Tanganyika achieved independence, marking a significant step towards self-determination.
The Birth of Tanzania: Tanganyika’s independence was not the end of its journey. In 1964, it merged with the island nation of Zanzibar to form the United Republic of Tanzania. This union, driven by the desire for unity and economic strength, created a new chapter in the history of the region.
The Tanganyika Map: A Visual Representation of a Transformative Era
The Tanganyika map, a cartographic representation of the territory during its colonial and independent eras, serves as a valuable historical document. It provides a visual framework for understanding the boundaries, demographics, and political evolution of the region. The map’s significance lies in its ability to:
- Illustrate the Geographical Scope: The map clearly defines the physical boundaries of Tanganyika, encompassing vast stretches of land, diverse ecosystems, and a rich cultural tapestry.
- Highlight Colonial Influence: The map reveals the impact of colonial administration, showcasing the division of the territory into administrative districts, the establishment of infrastructure, and the presence of European settlements.
- Trace the Path to Independence: The map serves as a historical marker, depicting the gradual transition from colonial rule to self-governance, capturing the milestones and challenges of the independence movement.
- Uncover Ethnic Diversity: The map can be utilized to study the distribution of various ethnic groups within Tanganyika, providing insights into the social and cultural landscape of the region.
- Offer Insights into Economic Development: The map can be used to analyze the distribution of resources, infrastructure, and economic activity within Tanganyika, shedding light on the region’s economic potential and challenges.
The Enduring Relevance of the Tanganyika Map
Despite the passage of time, the Tanganyika map remains a relevant and valuable tool for understanding the history and present-day reality of Tanzania. Its significance extends beyond mere historical documentation, providing a platform for:
- Historical Research: The map serves as a primary source for researchers exploring the colonial era, the independence movement, and the early years of Tanzania.
- Educational Purposes: The map provides a visual representation of the past, making it an effective tool for teaching students about the history of Tanzania and the complexities of colonial rule.
- Cultural Understanding: The map can be used to understand the cultural diversity of Tanzania, tracing the origins and distribution of different ethnic groups and their traditions.
- Economic Analysis: The map can be utilized to analyze the historical development of infrastructure, resource distribution, and economic activity, providing insights into the challenges and opportunities for future development.
FAQs about the Tanganyika Map
Q: What were the main reasons for the German colonization of Tanganyika?
A: The German colonization of Tanganyika was driven by a combination of factors, including:
- Economic Interests: The German government sought to exploit the region’s natural resources, particularly ivory, rubber, and coffee.
- Strategic Considerations: Tanganyika’s strategic location on the East African coast offered access to important trade routes and provided a base for expanding German influence in the region.
- National Prestige: Colonization was seen as a way to enhance Germany’s international standing and prestige as a powerful nation.
Q: What were the major challenges faced by Tanganyika during the British mandate?
A: The British mandate period in Tanganyika was marked by several challenges, including:
- Economic Exploitation: The British continued to extract resources from Tanganyika, often at the expense of local populations.
- Social Inequality: The British administration maintained a system of racial segregation and discrimination, limiting opportunities for Africans.
- Political Suppression: Nationalist movements advocating for independence were often suppressed, leading to unrest and resistance.
Q: How did the Tanganyika African National Union (TANU) contribute to independence?
A: TANU played a pivotal role in achieving independence for Tanganyika. Its key contributions included:
- Mobilizing the Population: TANU successfully rallied support for independence among the Tanganyikan people through grassroots organizing and political campaigns.
- Advocating for Self-Governance: TANU consistently advocated for self-determination and opposed colonial rule, pressuring the British government to grant independence.
- Negotiating with the British: TANU engaged in negotiations with the British government, leading to the eventual transfer of power and the establishment of an independent Tanganyika.
Q: What were the main reasons for the union between Tanganyika and Zanzibar?
A: The union between Tanganyika and Zanzibar was driven by several factors, including:
- Political Unity: The union aimed to create a larger and more powerful nation, capable of asserting its independence on the international stage.
- Economic Integration: The union sought to integrate the economies of Tanganyika and Zanzibar, fostering trade and economic growth.
- Social Cohesion: The union aimed to promote social cohesion and national unity, bringing together different ethnic groups and regions under a single banner.
Tips for Understanding the Tanganyika Map
- Examine the Geographical Features: Pay attention to the physical features depicted on the map, such as rivers, mountains, and lakes, to understand the geography of the region.
- Identify Administrative Boundaries: Observe the boundaries of administrative districts, provinces, or other divisions to understand the organization of the territory.
- Locate Key Cities and Towns: Identify major cities and towns on the map to gain insights into the population distribution and economic activity.
- Study the Infrastructure: Analyze the presence of roads, railways, ports, and other infrastructure to understand the development of the region.
- Compare Different Versions: Compare different versions of the Tanganyika map from different historical periods to observe the changes in boundaries, infrastructure, and other features.
Conclusion
The Tanganyika map, a historical artifact, serves as a valuable window into the past, providing a visual representation of a transformative period in the history of Tanzania. It highlights the complex interplay of colonial influence, nationalist movements, and the eventual achievement of independence. By understanding the Tanganyika map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the historical processes that shaped the modern nation of Tanzania, its cultural diversity, and its enduring legacy. This historical understanding is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in the pursuit of a prosperous and equitable future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Past: A Comprehensive Look at the Tanganyika Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
