Understanding the Arizona-Mexico Border: A Geographical and Historical Perspective
Related Articles: Understanding the Arizona-Mexico Border: A Geographical and Historical Perspective
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Arizona-Mexico Border: A Geographical and Historical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Arizona-Mexico Border: A Geographical and Historical Perspective

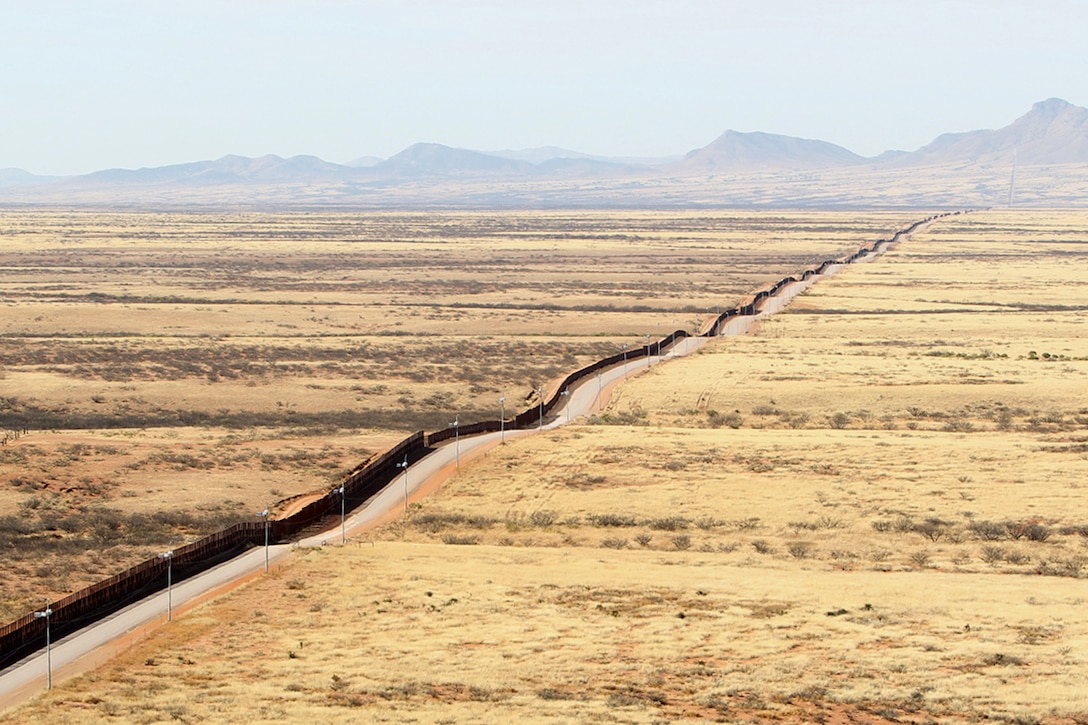
The Arizona-Mexico border, spanning over 370 miles, is a complex and dynamic boundary with a rich history and significant present-day implications. It is not merely a geographical line on a map, but a vibrant tapestry woven with threads of culture, economics, and politics. This article delves into the intricacies of the Arizona-Mexico border, exploring its geographic features, historical significance, and its current relevance in the context of immigration, trade, and cultural exchange.
The Geography of the Border:
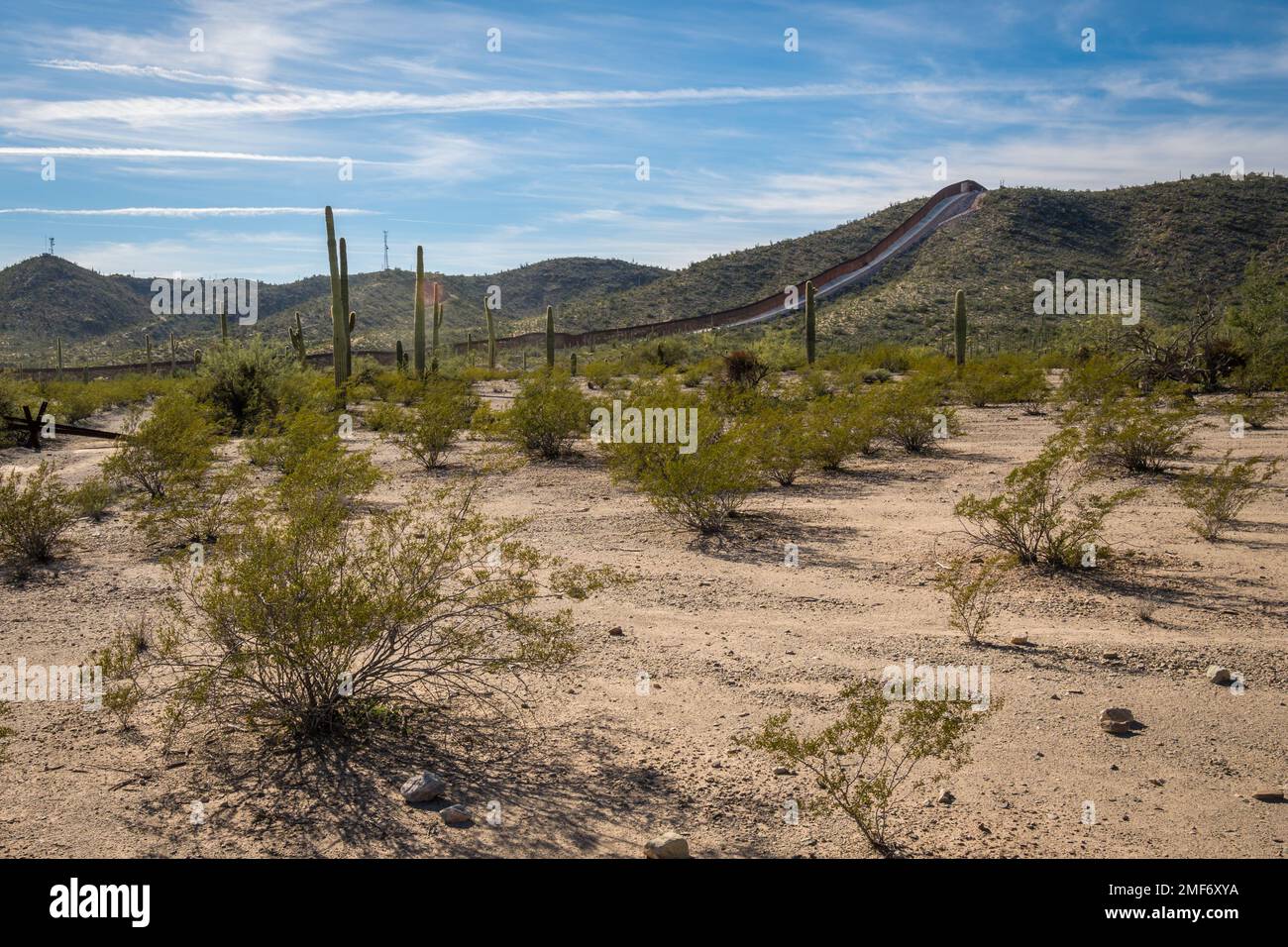
The Arizona-Mexico border traverses diverse landscapes, ranging from the rugged Sonoran Desert to the towering peaks of the Huachuca Mountains. This geographical diversity presents unique challenges and opportunities for border management, economic development, and environmental conservation.
- Sonoran Desert: The majority of the border lies within the Sonoran Desert, characterized by its extreme temperatures, sparse vegetation, and vast stretches of sand and rock. This harsh environment poses significant challenges for border patrol and poses risks to migrants attempting to cross.
- Mountains: The Huachuca Mountains, the Santa Catalina Mountains, and the San Rafael Valley offer dramatic elevation changes, creating natural barriers and influencing the flow of people and goods.
- Rivers: The Colorado River, the Gila River, and the San Pedro River provide crucial water sources for both sides of the border and serve as natural boundaries in certain sections.
Historical Context:
The Arizona-Mexico border has witnessed a long and complex history, shaped by territorial disputes, political shifts, and cultural exchanges.
- Pre-Colonial Era: Before the arrival of European colonizers, the region was inhabited by indigenous groups, such as the Tohono O’odham, the Apache, and the Yaqui, who freely traversed the land.
- Spanish Colonization: Following the Spanish conquest of Mexico, the region became part of New Spain. The border was established in 1848 with the signing of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which ceded vast territories to the United States, including what is now Arizona.
- Immigration and Development: The border has witnessed significant waves of immigration, primarily from Mexico, driven by economic opportunities and political instability. This has shaped the cultural landscape of Arizona and fostered a strong economic relationship with Mexico.
Current Relevance:
The Arizona-Mexico border remains a focal point of national and international attention, with ongoing discussions about immigration, trade, and security.
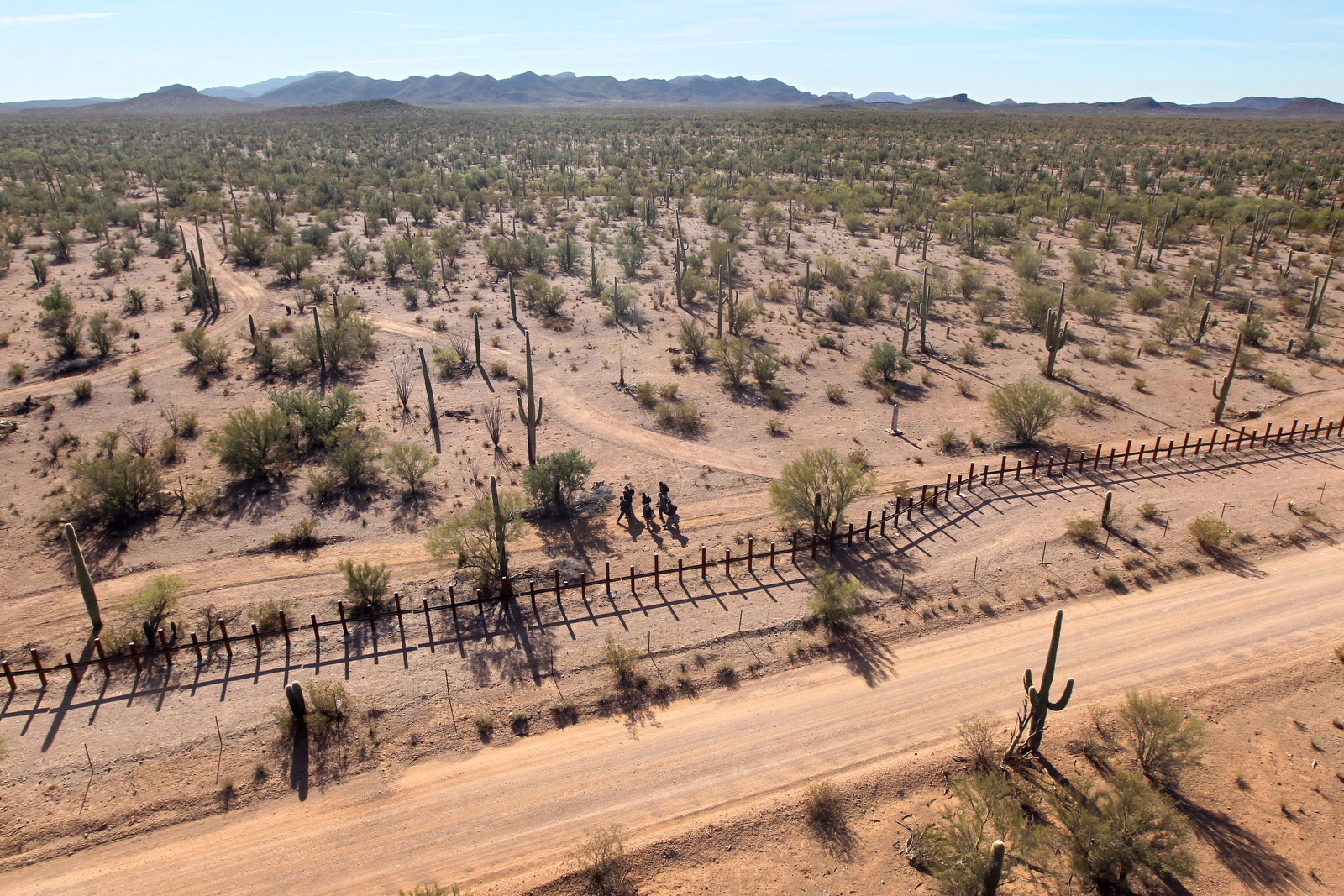
- Immigration: The border is a major entry point for undocumented migrants seeking a better life in the United States. This issue has fueled political debates and prompted the implementation of stricter border security measures.
- Trade: The border facilitates significant trade between the United States and Mexico, with Arizona playing a crucial role in the flow of goods and services. The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and its successor, the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), have further strengthened economic ties.
- Cultural Exchange: The border is a vibrant hub of cultural exchange, with communities on both sides sharing traditions, languages, and ways of life. This cultural richness contributes to the unique identity of the border region.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Arizona-Mexico border presents both challenges and opportunities for both countries.
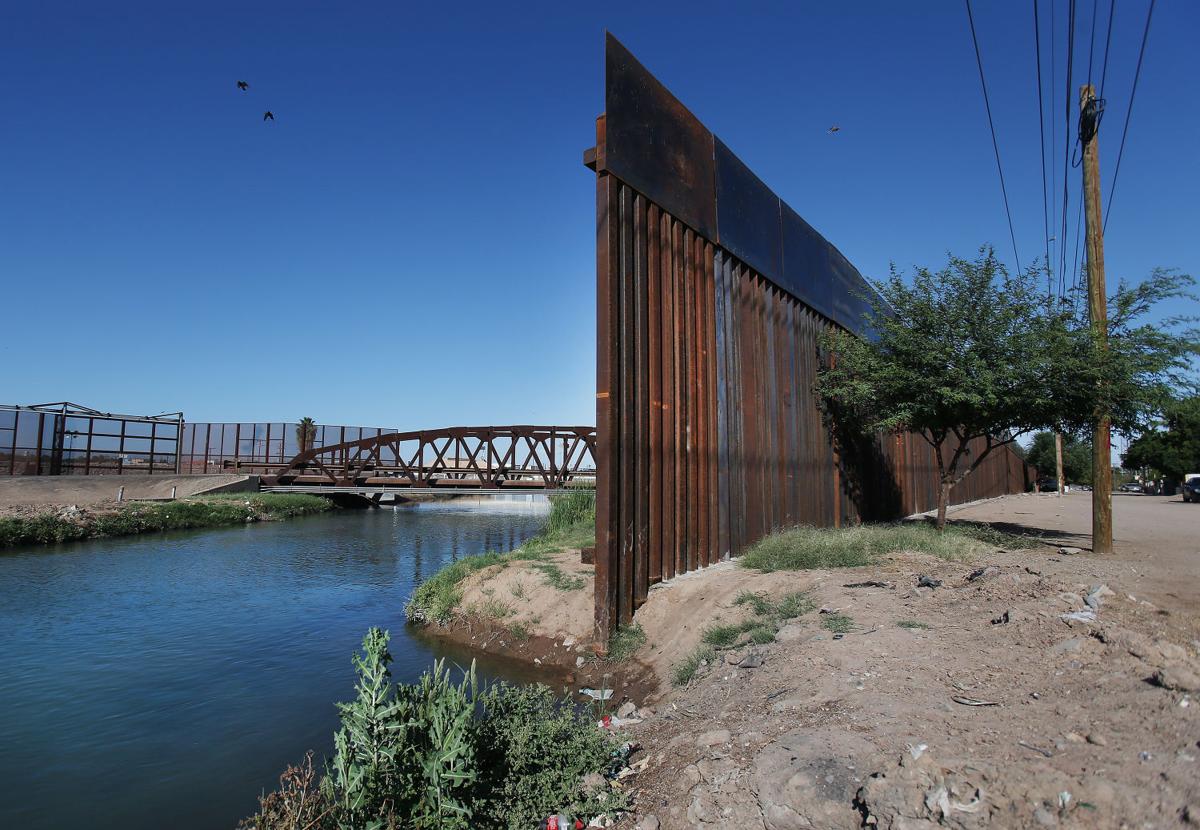
- Border Security: Maintaining border security while respecting human rights remains a complex challenge. The use of physical barriers, increased border patrol presence, and technological advancements are ongoing efforts to address this issue.
- Economic Development: The border offers opportunities for economic growth through cross-border trade, tourism, and investment. However, challenges such as infrastructure limitations and regulatory differences need to be addressed.
- Environmental Protection: The shared environment of the border region requires collaborative efforts to protect natural resources, address climate change, and manage water resources.
FAQs:
1. What is the significance of the Arizona-Mexico border?
The Arizona-Mexico border holds immense significance due to its historical, cultural, and economic importance. It serves as a bridge between two nations, facilitating trade, migration, and cultural exchange.
2. What are the major challenges faced at the Arizona-Mexico border?
The border faces challenges related to immigration, security, economic development, and environmental protection. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration and understanding between both countries.
3. What are the opportunities for economic development at the Arizona-Mexico border?
The border presents opportunities for economic growth through cross-border trade, tourism, and investment. However, infrastructure development and regulatory harmonization are crucial for maximizing these opportunities.
4. What are the cultural implications of the Arizona-Mexico border?
The border is a vibrant hub of cultural exchange, with communities on both sides sharing traditions, languages, and ways of life. This cultural richness contributes to the unique identity of the border region.
5. What are the environmental issues associated with the Arizona-Mexico border?
The shared environment of the border region requires collaborative efforts to protect natural resources, address climate change, and manage water resources.
Tips:
- Travel Responsibly: When visiting the Arizona-Mexico border, be aware of the security measures in place and adhere to all regulations. Respect the cultures and traditions of the communities you encounter.
- Support Local Businesses: Patronize local businesses on both sides of the border to contribute to the economic well-being of the region.
- Engage in Cultural Exchange: Participate in cultural events and activities that promote understanding and appreciation of the diverse cultures of the border region.
- Promote Environmental Sustainability: Support initiatives that promote environmental protection and sustainable development in the border region.
Conclusion:
The Arizona-Mexico border is a dynamic and complex landscape with a rich history and significant present-day implications. Understanding its geography, history, and current challenges is crucial for fostering collaboration, promoting economic development, and preserving the cultural richness of the region. By working together, the United States and Mexico can leverage the opportunities presented by the border to create a more prosperous and secure future for all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Arizona-Mexico Border: A Geographical and Historical Perspective. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
