Understanding Map-Dot-Fingerprint Corneal Dystrophy: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Map-Dot-Fingerprint Corneal Dystrophy: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Map-Dot-Fingerprint Corneal Dystrophy: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Map-Dot-Fingerprint Corneal Dystrophy: A Comprehensive Guide
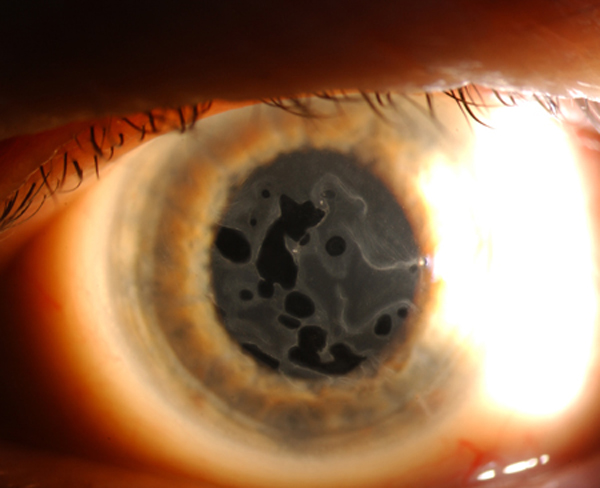
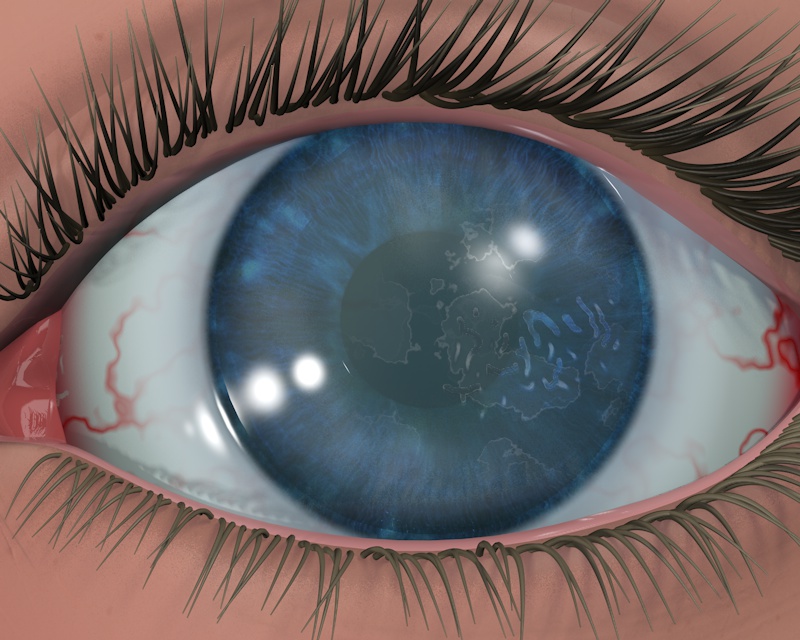
Map-dot-fingerprint corneal dystrophy, often referred to as MDFFCD, is a rare, inherited eye condition characterized by distinctive changes in the cornea, the clear outer layer of the eye. This condition primarily affects the corneal epithelium, the outermost layer of the cornea, and can significantly impact vision. While it is not life-threatening, MDFFCD can cause discomfort and visual impairment, requiring careful management and treatment.
The Nature of the Condition
MDFFCD is a form of corneal dystrophy, a group of disorders that affect the cornea’s structure and function. The condition is caused by mutations in specific genes responsible for producing proteins vital for maintaining corneal health. These mutations lead to the abnormal accumulation of material in the corneal epithelium, resulting in the characteristic features of MDFFCD.
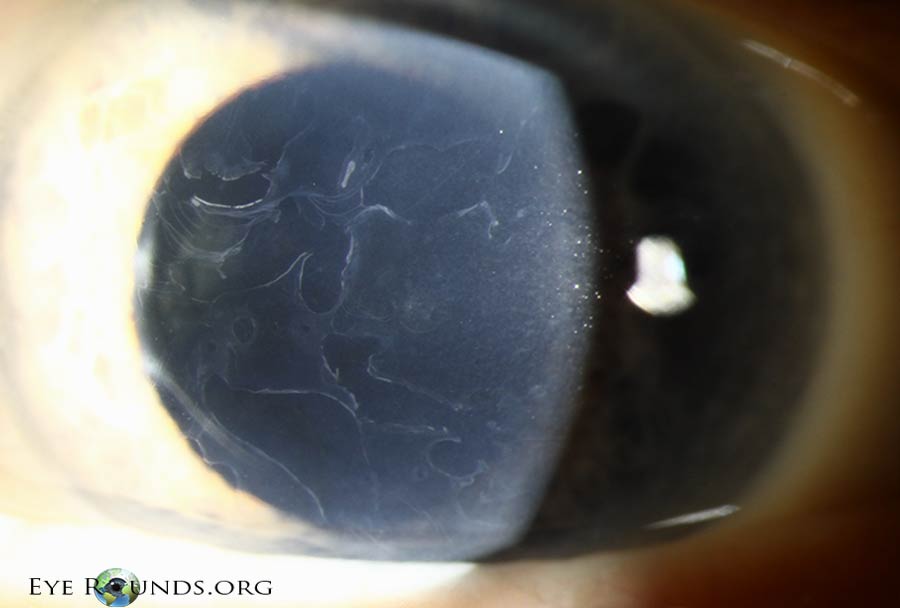
Distinctive Features of MDFFCD
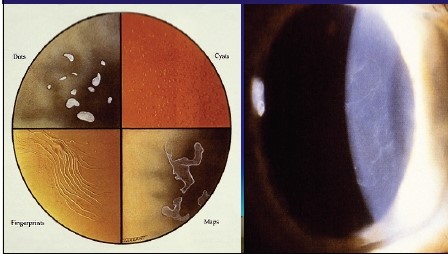
The name "map-dot-fingerprint" aptly describes the unique appearance of the corneal changes associated with this condition. These include:
- Map-like Opacities: These appear as irregular, branching patterns resembling a geographical map. They are often seen in the central and peripheral cornea.
- Dot-like Opacities: These are small, round, and scattered throughout the cornea, appearing as tiny dots.
- Fingerprint-like Opacities: These resemble fingerprints, with curved lines and ridges extending across the cornea.
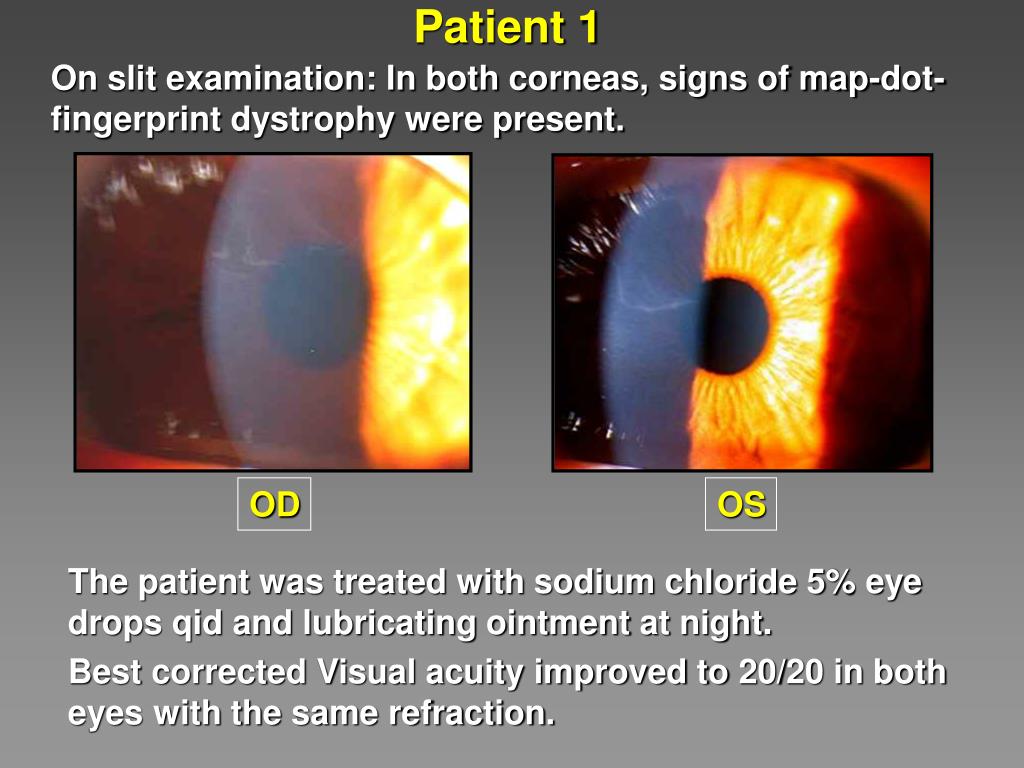
These opacities can be seen through a slit lamp, a specialized microscope used by ophthalmologists to examine the eye. The severity of these opacities varies, ranging from mild, barely noticeable changes to dense, widespread opacities that significantly impair vision.
Symptoms and Impact on Vision
MDFFCD can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Blurred Vision: This is the most common symptom, particularly in cases with dense opacities.
- Glare and Light Sensitivity: The opacities can scatter light, making it difficult to see in bright environments.
- Dryness and Irritation: The corneal changes can affect the tear film, leading to dryness and irritation.
- Foreign Body Sensation: Some individuals experience a feeling of something in their eye, even though no foreign object is present.
The severity of symptoms and impact on vision depend on the extent and density of the corneal opacities. In some cases, the condition may be asymptomatic, while in others, it can significantly impair daily activities.
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosing MDFFCD typically involves a comprehensive eye examination by an ophthalmologist. This examination includes:
- Visual Acuity Testing: This assesses the patient’s ability to see at different distances.
- Slit Lamp Examination: This allows the ophthalmologist to visualize the corneal opacities and other eye structures.
- Corneal Topography: This specialized imaging technique maps the corneal surface, providing detailed information about its shape and curvature.
- Family History: A thorough family history can help identify potential genetic predisposition.
Management of MDFFCD focuses on addressing symptoms and maintaining visual function. Treatment options include:
- Lubricating Eye Drops: These help alleviate dryness and irritation.
- Topical Medications: Eye drops containing corticosteroids or cyclosporine can reduce inflammation and improve corneal clarity.
- Contact Lenses: In some cases, contact lenses can improve vision by smoothing the irregular corneal surface.
- Corneal Transplant (Keratoplasty): This surgical procedure replaces the affected cornea with a healthy donor cornea. It is typically reserved for severe cases with significant visual impairment.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Management
Early diagnosis and management of MDFFCD are crucial for several reasons:
- Preventing Vision Loss: Early intervention can help prevent further deterioration of vision.
- Managing Symptoms: Treatment can alleviate discomfort and improve quality of life.
- Genetic Counseling: Individuals with MDFFCD should consider genetic counseling to understand the risks of passing the condition to their children.
FAQs About Map-Dot-Fingerprint Corneal Dystrophy
1. Is MDFFCD contagious?
No, MDFFCD is not contagious. It is an inherited condition, not an infectious disease.
2. Can MDFFCD be cured?
There is no cure for MDFFCD, but treatment options can manage symptoms and prevent vision loss.
3. How common is MDFFCD?
MDFFCD is a rare condition, affecting a small percentage of the population.
4. What is the life expectancy of someone with MDFFCD?
MDFFCD does not affect life expectancy. While it can cause vision impairment, it is not a life-threatening condition.
5. Can MDFFCD be prevented?
Currently, there is no way to prevent MDFFCD as it is an inherited condition.
Tips for Managing MDFFCD
- Regular Eye Exams: Schedule regular eye exams to monitor the condition and detect any changes early.
- Lubricating Eye Drops: Use lubricating eye drops as needed to alleviate dryness and irritation.
- Protect Your Eyes: Wear sunglasses and protective eyewear to shield your eyes from harmful UV rays and other irritants.
- Avoid Eye Rubbing: Avoid rubbing your eyes as this can exacerbate irritation and worsen symptoms.
- Consult Your Ophthalmologist: Discuss any concerns or changes in your vision with your ophthalmologist.
Conclusion
Map-dot-fingerprint corneal dystrophy is a rare, inherited condition that can cause visual impairment and discomfort. While there is no cure, early diagnosis and management can help prevent vision loss and improve quality of life. Regular eye exams, proper eye care, and close communication with your ophthalmologist are essential for managing this condition effectively. Understanding the nature of MDFFCD and its potential impact can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards preserving their vision and maintaining overall eye health.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Map-Dot-Fingerprint Corneal Dystrophy: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!