The Alaskan Pipeline: A Modern Engineering Marvel and Lifeline for the North
Related Articles: The Alaskan Pipeline: A Modern Engineering Marvel and Lifeline for the North
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Alaskan Pipeline: A Modern Engineering Marvel and Lifeline for the North. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Alaskan Pipeline: A Modern Engineering Marvel and Lifeline for the North
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Alaskan Pipeline: A Modern Engineering Marvel and Lifeline for the North
- 3.1 A Glimpse into the Alaskan Pipeline Map
- 3.2 Understanding the Importance and Benefits
- 3.3 Addressing Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.4 Tips for Understanding the Alaskan Pipeline Map
- 3.5 Conclusion: A Legacy of Engineering and Resource Management
- 4 Closure
The Alaskan Pipeline: A Modern Engineering Marvel and Lifeline for the North

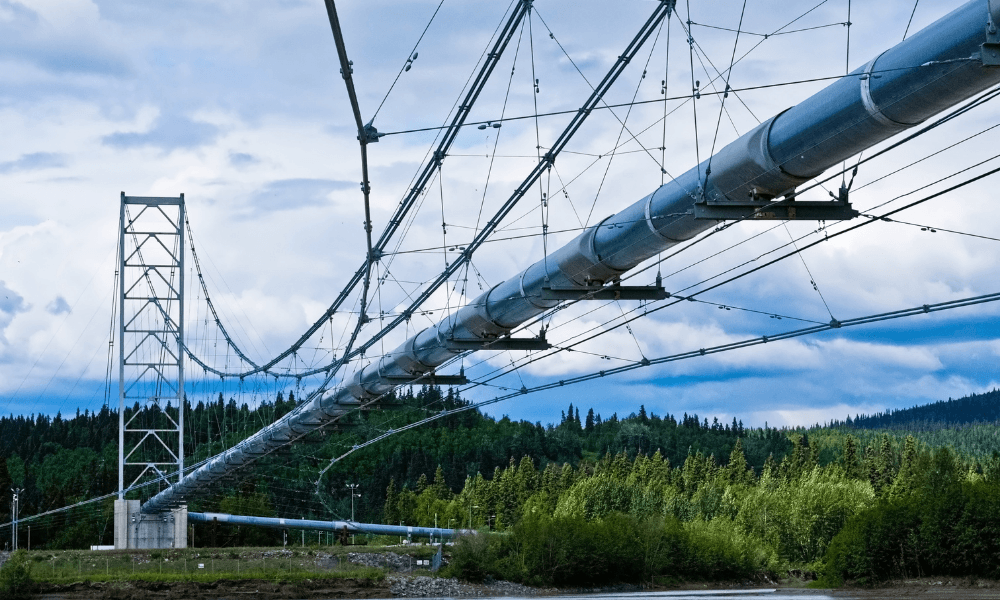
The Trans-Alaska Pipeline System (TAPS) stands as a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of energy resources. Stretching over 800 miles across the rugged Alaskan wilderness, this monumental pipeline system connects the Prudhoe Bay oil fields on the North Slope to the port of Valdez on the southern coast, facilitating the transportation of crude oil to refineries and markets worldwide.
A Glimpse into the Alaskan Pipeline Map
The Alaskan Pipeline map is a visual representation of this intricate engineering marvel. It showcases the pipeline’s serpentine route, winding through diverse landscapes, from the frozen tundra and permafrost to mountainous terrain and dense forests.
Key elements depicted on the Alaskan Pipeline map include:
- The Prudhoe Bay Oil Fields: The source of the oil transported through the pipeline, located on the North Slope of Alaska.
- The Trans-Alaska Pipeline: The main artery of the system, traversing the state from north to south.
- Pump Stations: Strategically placed along the pipeline to maintain pressure and ensure continuous oil flow.
- Valdez Terminal: The southern terminus of the pipeline, where oil is loaded onto tankers for shipment to refineries.
- Supporting Infrastructure: A network of roads, bridges, and other facilities necessary for the operation and maintenance of the pipeline.
Beyond the physical representation, the Alaskan Pipeline map provides valuable insights into:
- The geographical challenges: The map highlights the extreme terrain and harsh climate that engineers had to overcome in constructing the pipeline.
- Environmental considerations: It reveals the pipeline’s proximity to sensitive ecosystems and the measures taken to mitigate potential environmental impacts.
- Economic significance: The map illustrates the vital role the pipeline plays in Alaska’s economy, providing jobs and revenue for the state.
Understanding the Importance and Benefits
The Alaskan Pipeline has played a transformative role in the economic and social landscape of Alaska. Its construction and operation have brought significant benefits, including:
- Economic Growth: The pipeline has created thousands of jobs and generated substantial revenue for the state, contributing to its economic development.
- Energy Security: It provides a reliable source of energy for the United States, reducing dependence on foreign oil imports.
- Infrastructure Development: The pipeline’s construction spurred the development of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure, improving transportation and communication in the state.
- Technological Advancements: The engineering challenges posed by the pipeline’s construction led to the development of innovative technologies and techniques, advancing the field of pipeline engineering.
Addressing Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why was the Alaskan Pipeline built?
The pipeline was built to transport crude oil from the Prudhoe Bay oil fields to the port of Valdez, facilitating its shipment to refineries and markets. The discovery of vast oil reserves in the North Slope presented a unique opportunity to tap into a new source of energy, but the remoteness of the region posed significant logistical challenges. The pipeline was conceived as the most efficient solution to overcome these challenges and bring Alaskan oil to market.
2. What are the environmental impacts of the Alaskan Pipeline?
The pipeline’s construction and operation have had some environmental impacts, including habitat fragmentation, disruption of wildlife migration patterns, and the potential for oil spills. However, extensive environmental mitigation measures were implemented during the construction phase, and ongoing monitoring and maintenance efforts are crucial for minimizing potential risks.
3. How does the Alaskan Pipeline operate?
The pipeline operates by pumping crude oil from the Prudhoe Bay oil fields to the Valdez terminal. The oil is heated and pressurized to maintain its fluidity and flow through the pipeline. Pump stations strategically located along the route ensure continuous flow, while valves and control systems regulate the oil’s movement and prevent spills.
4. What are the challenges of maintaining the Alaskan Pipeline?
Maintaining the pipeline in the harsh Alaskan environment presents significant challenges. Extreme temperatures, permafrost conditions, and seismic activity require specialized equipment and techniques to ensure the pipeline’s integrity and prevent leaks. Regular inspections, repairs, and upgrades are essential to ensure the pipeline’s long-term functionality.
5. What is the future of the Alaskan Pipeline?
The future of the Alaskan Pipeline is uncertain, as global energy markets and environmental concerns continue to evolve. The pipeline’s continued operation will depend on factors such as oil production levels, market demand, and the effectiveness of environmental mitigation measures.
Tips for Understanding the Alaskan Pipeline Map
- Use a map with clear labels: Look for a map that clearly identifies key features, such as pump stations, the pipeline route, and the Valdez terminal.
- Focus on the scale: Pay attention to the scale of the map to understand the vast distances involved in the pipeline’s construction and operation.
- Consider the surrounding environment: Examine the map in relation to surrounding geographical features, such as mountains, rivers, and forests, to appreciate the challenges faced by engineers.
- Research the history: Learn about the history of the pipeline’s construction and the environmental and economic considerations that shaped its development.
- Explore the pipeline’s impact: Research the pipeline’s impact on Alaska’s economy, environment, and social fabric.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Engineering and Resource Management
The Alaskan Pipeline stands as a remarkable feat of engineering, a testament to human ingenuity in overcoming challenging terrain and environmental conditions. It has played a vital role in Alaska’s economic development and energy security, but its future remains subject to evolving energy markets and environmental considerations. The Alaskan Pipeline map provides a valuable window into this complex system, highlighting its geographical challenges, environmental impacts, and economic significance. As we continue to explore and utilize natural resources, understanding the complexities of projects like the Alaskan Pipeline is crucial for informed decision-making and sustainable development.
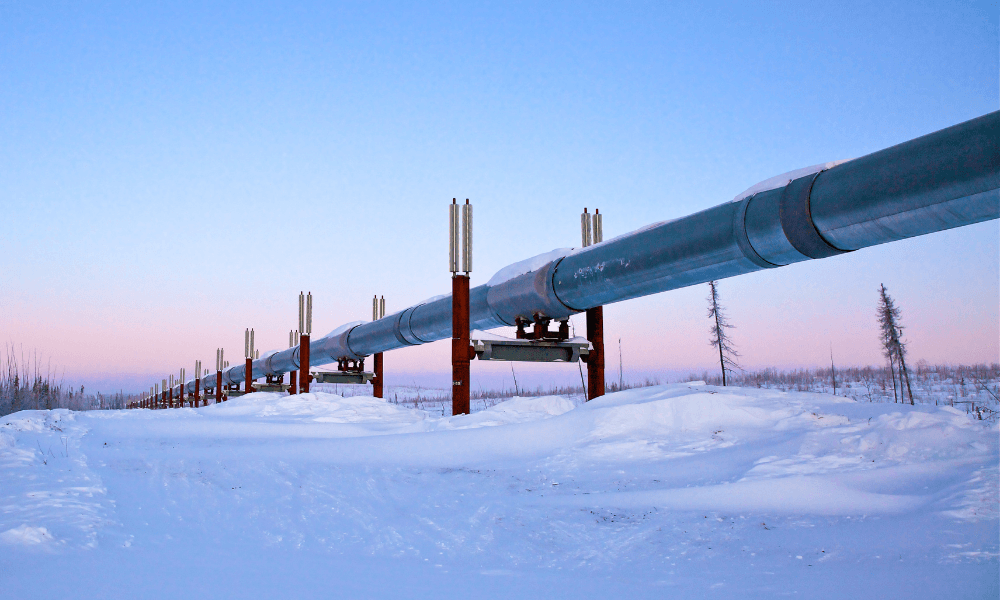
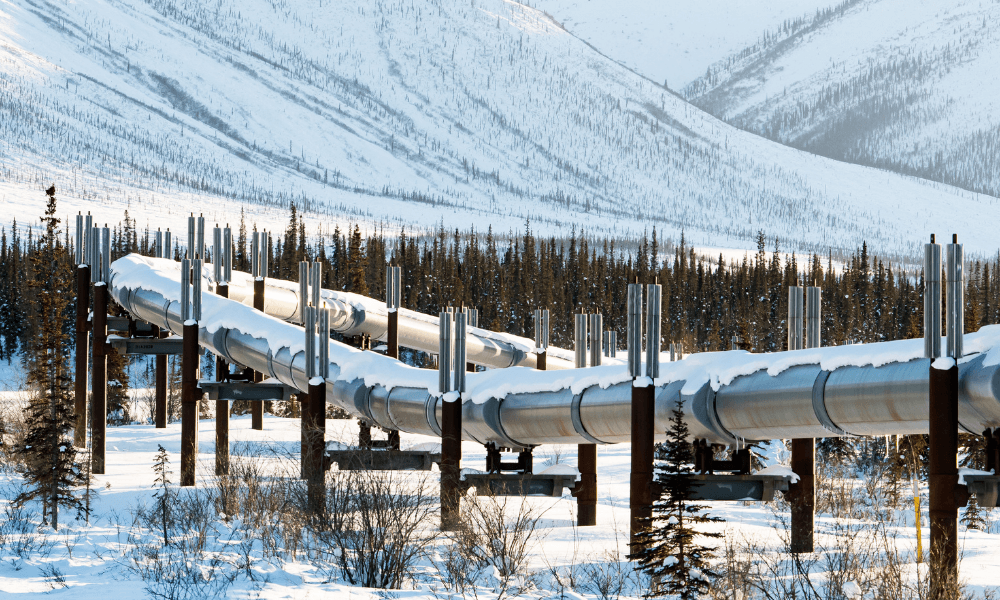
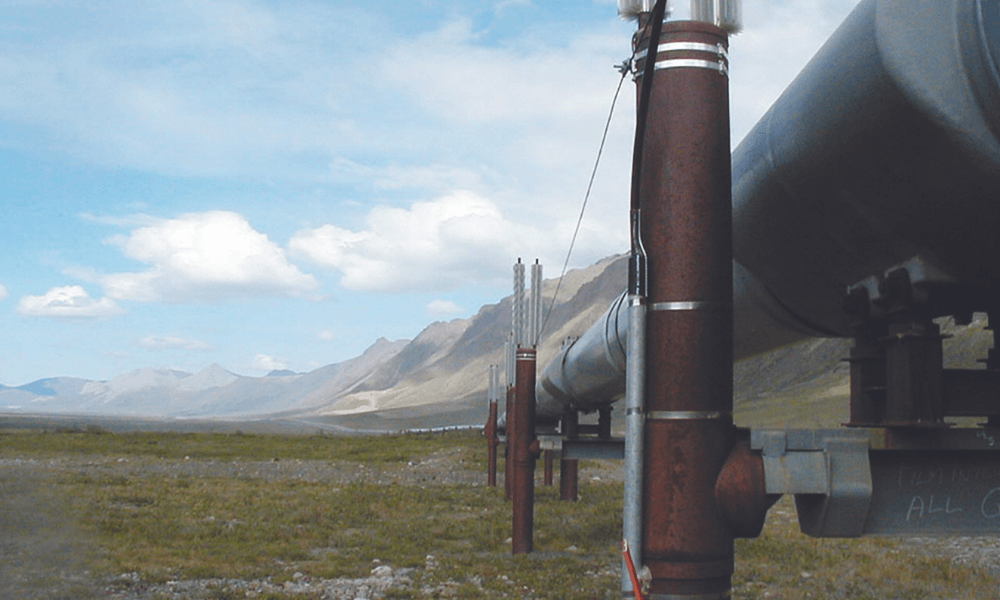
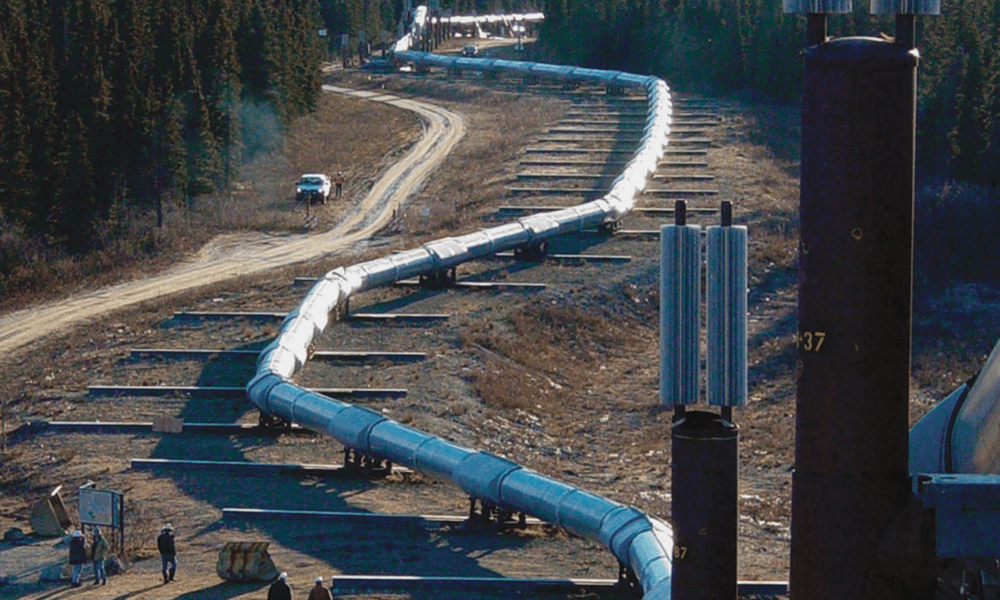






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Alaskan Pipeline: A Modern Engineering Marvel and Lifeline for the North. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!