Navigating the Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Arctic Ice Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Arctic Ice Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Arctic Ice Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Arctic Ice Map
The Arctic, a vast and unforgiving region encircling the North Pole, is characterized by its iconic sea ice cover. This dynamic layer of frozen seawater plays a crucial role in regulating global climate, influencing weather patterns, and supporting unique ecosystems. As climate change continues to impact the planet, the Arctic sea ice cover has been shrinking at an alarming rate, leading to significant environmental and societal consequences.
To monitor and understand these changes, scientists and researchers rely on Arctic ice maps. These maps provide a visual representation of the extent, thickness, and age of sea ice at a given time, offering valuable insights into the health and dynamics of the Arctic environment.
Understanding the Arctic Ice Map:
An Arctic ice map is essentially a visual representation of the sea ice cover in the Arctic region. It is typically generated using satellite imagery, which captures data on the extent, thickness, and age of the ice. These maps are crucial tools for understanding the following:
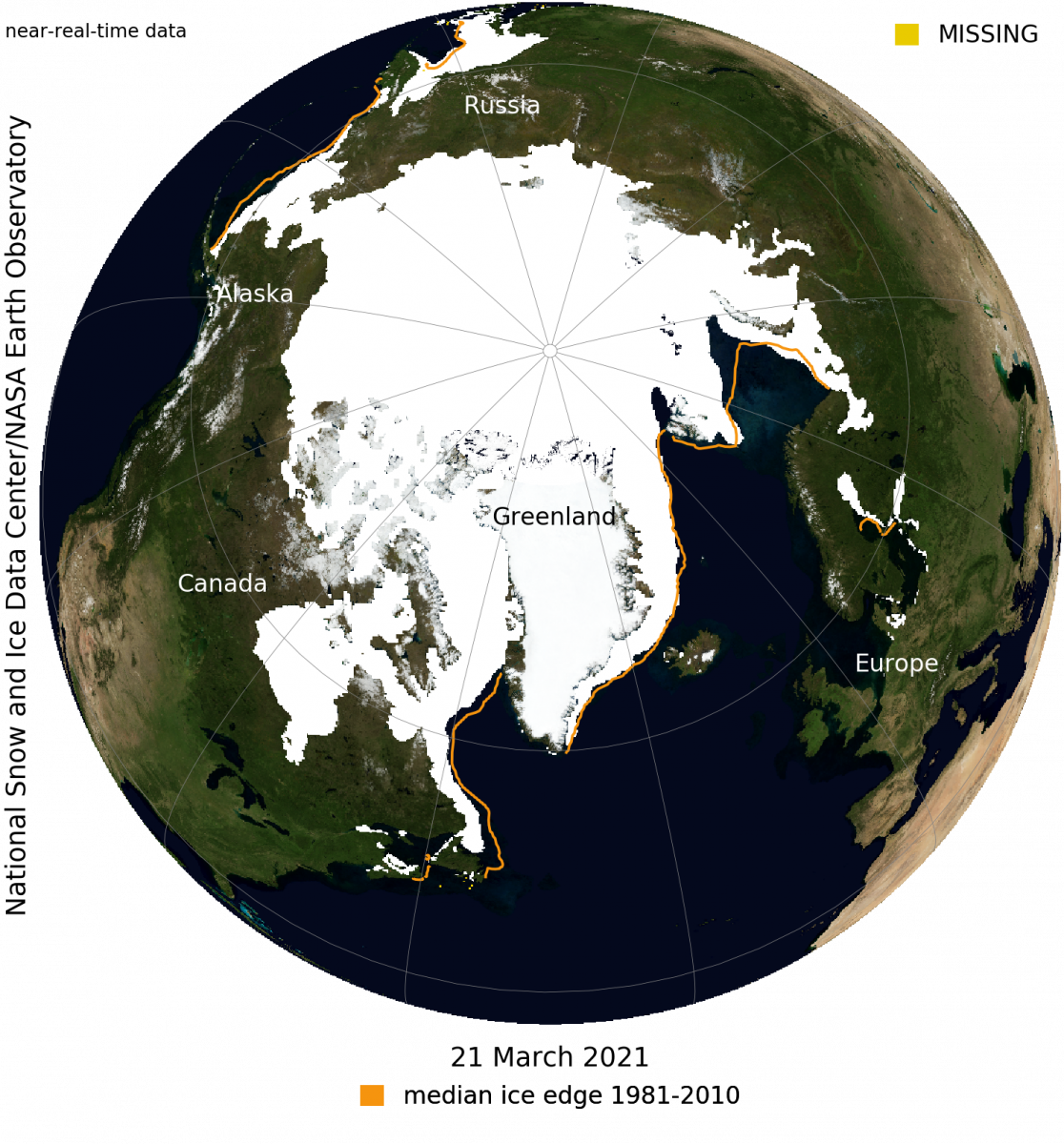
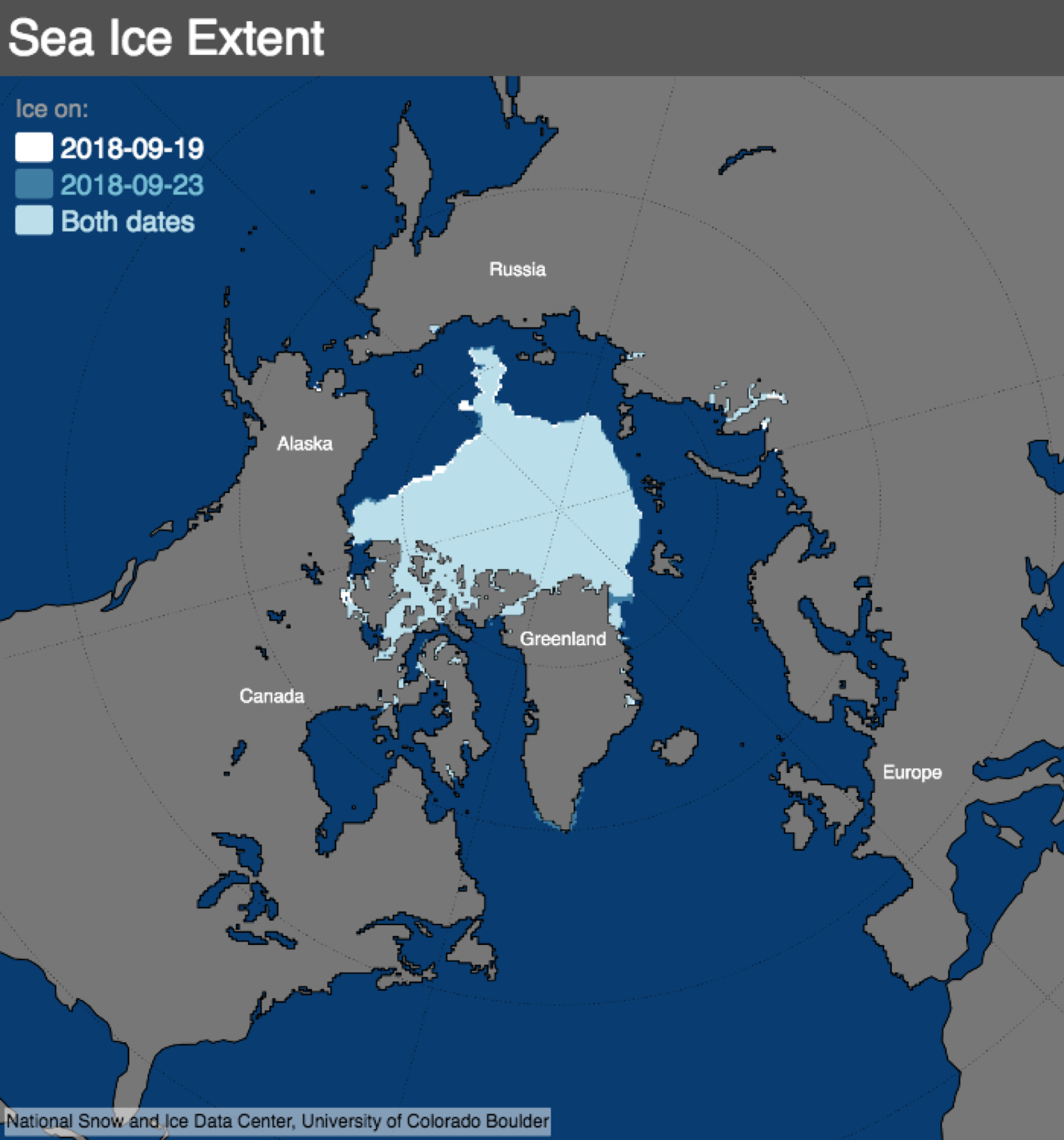
- Sea Ice Extent: This refers to the total area of the ocean covered by ice. It is a key indicator of the overall health of the Arctic ice cover.
- Sea Ice Thickness: This refers to the depth of the ice. Thicker ice is older and more resistant to melting, while thinner ice is younger and more vulnerable to change.
- Sea Ice Age: This refers to the time a particular piece of ice has been frozen. Older ice is typically thicker and more resilient, while younger ice is thinner and more prone to melting.
The Importance of Arctic Ice Maps:
Arctic ice maps play a crucial role in various fields:
- Climate Change Research: By tracking changes in sea ice extent, thickness, and age, scientists can gain a better understanding of the impact of climate change on the Arctic environment. This data is vital for predicting future climate change scenarios and developing mitigation strategies.
- Weather Forecasting: Sea ice plays a significant role in influencing weather patterns, particularly in the northern hemisphere. Ice maps provide valuable data for weather forecasting models, improving the accuracy of predictions.
- Navigation and Shipping: Sea ice conditions are critical for safe navigation in the Arctic. Ice maps provide information on ice extent and thickness, allowing ships to plan their routes and avoid hazardous ice conditions.
- Resource Management: The Arctic region is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals. Ice maps are essential for understanding the distribution and accessibility of these resources.
- Wildlife Conservation: Sea ice is vital for the survival of many Arctic species, including polar bears, seals, and walruses. Ice maps help scientists monitor the health of these populations and identify areas where conservation efforts are needed.
Data Sources for Arctic Ice Maps:
The data used to create Arctic ice maps comes from various sources:
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites equipped with radar and optical sensors capture images of the Arctic sea ice cover. These images provide data on the extent, thickness, and age of the ice.
- In-Situ Measurements: Scientists also collect data on sea ice conditions through in-situ measurements, such as drilling ice cores and deploying instruments to measure ice thickness.
- Model Simulations: Climate models can simulate the behavior of sea ice, providing valuable insights into its future evolution.
Types of Arctic Ice Maps:
There are various types of Arctic ice maps, each focusing on different aspects of the sea ice cover:
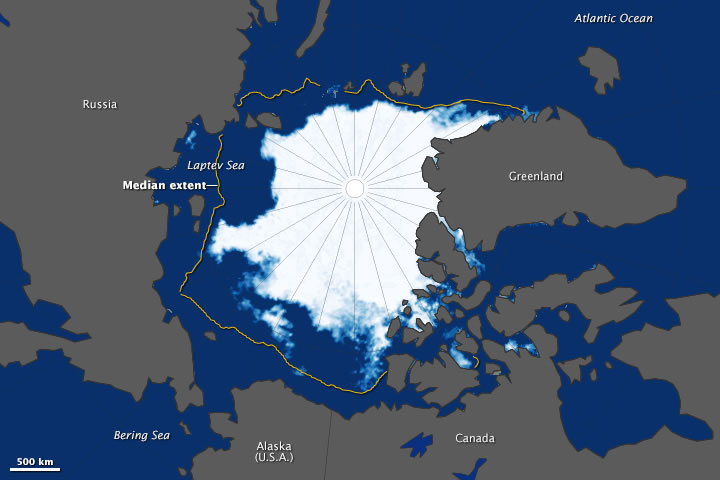
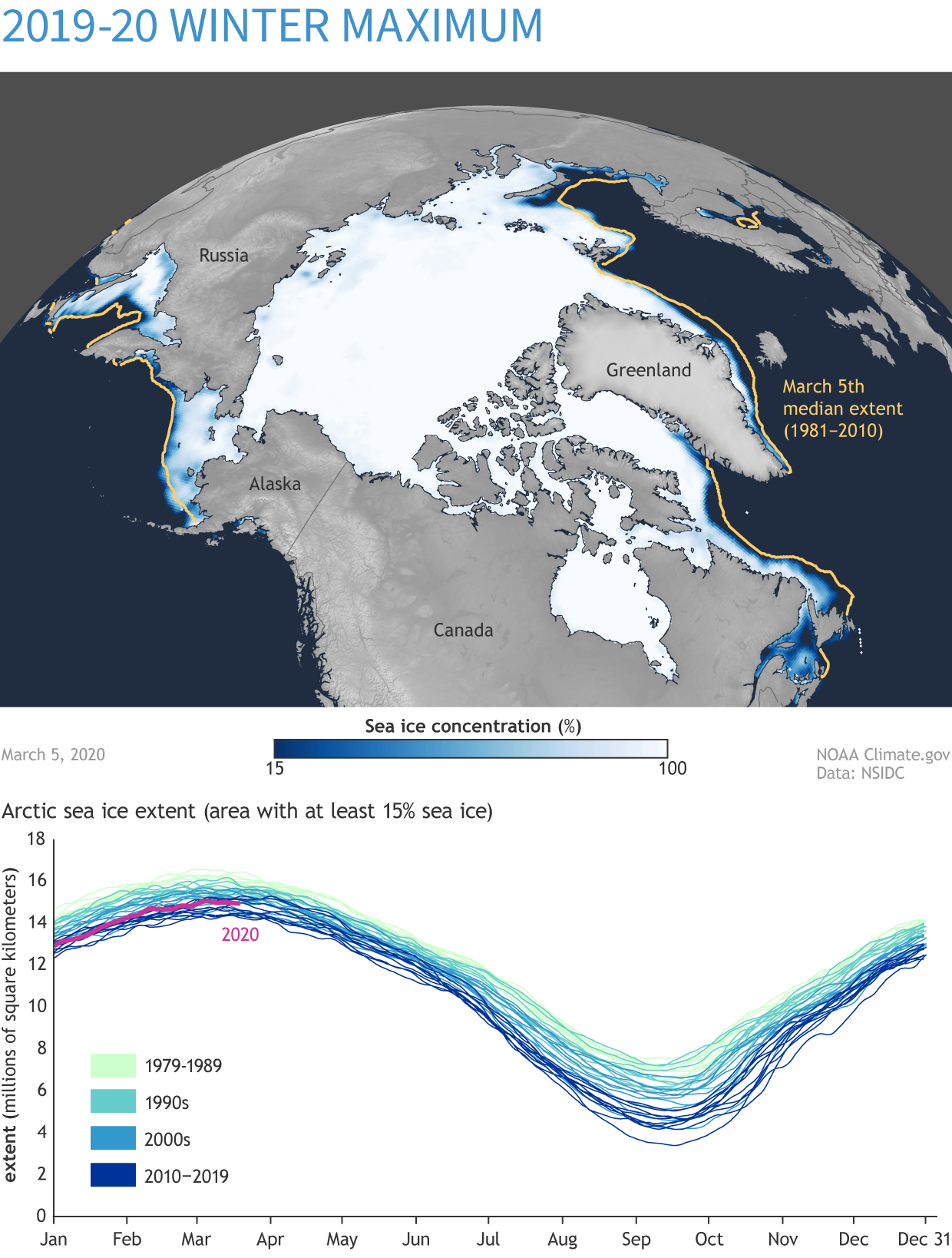
- Sea Ice Extent Maps: These maps show the total area of the ocean covered by sea ice.
- Sea Ice Concentration Maps: These maps indicate the percentage of ice cover within a given area.
- Sea Ice Thickness Maps: These maps depict the depth of the sea ice.
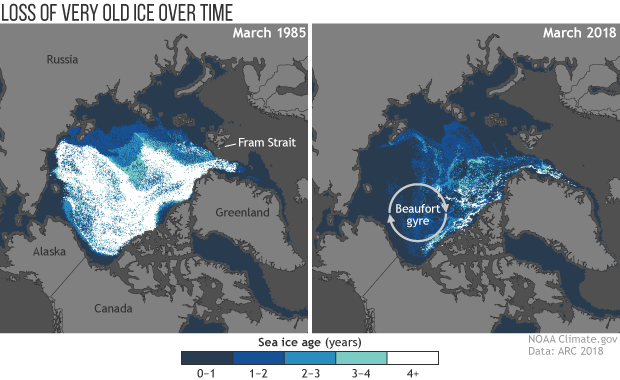
- Sea Ice Age Maps: These maps show the age of the sea ice, distinguishing between first-year ice and multi-year ice.
- Sea Ice Drift Maps: These maps illustrate the movement of sea ice, providing insights into ocean currents and wind patterns.
Current Trends and Challenges:
The Arctic is experiencing rapid changes due to climate change, with significant impacts on the sea ice cover. Key trends include:
- Decreasing Sea Ice Extent: The overall area of sea ice cover in the Arctic has been declining significantly over the past decades.
- Thinner Sea Ice: The average thickness of sea ice has been decreasing, leading to increased vulnerability to melting.
- Less Multi-Year Ice: The amount of multi-year ice (ice that has survived at least one summer melt season) is decreasing, further contributing to the overall decline in ice thickness.
These trends pose significant challenges for the Arctic environment, human activities, and the global climate.
FAQs on Arctic Ice Maps:
Q: What is the difference between sea ice and land ice?
A: Sea ice is frozen seawater that forms on the ocean surface, while land ice is frozen freshwater found on land, such as glaciers and ice sheets.
Q: Why is the Arctic sea ice cover important?
A: Sea ice plays a crucial role in regulating global climate, influencing weather patterns, and supporting unique ecosystems. It also provides a vital habitat for many Arctic species.
Q: How are Arctic ice maps created?
A: Arctic ice maps are typically created using satellite imagery, which captures data on the extent, thickness, and age of the ice.
Q: What is the impact of climate change on Arctic sea ice?
A: Climate change is causing the Arctic sea ice cover to shrink at an alarming rate, leading to significant environmental and societal consequences.
Q: How can I access Arctic ice maps?
A: Several organizations, including the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) and the European Space Agency (ESA), provide access to Arctic ice maps online.
Tips for Understanding Arctic Ice Maps:
- Pay attention to the scale: The scale of the map indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground.
- Look for the legend: The legend explains the different colors and symbols used on the map.
- Consider the time of year: Sea ice extent varies significantly throughout the year, so it is important to consider the time of year when interpreting the map.
- Compare different maps: Comparing maps from different years or different sources can help identify trends and changes in sea ice conditions.
Conclusion:
Arctic ice maps are essential tools for understanding the health and dynamics of the Arctic environment. They provide invaluable insights into the impact of climate change on the region, influencing research, weather forecasting, navigation, resource management, and wildlife conservation. As the Arctic continues to change, these maps will play an increasingly vital role in informing policy decisions and ensuring the sustainable management of this critical region.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Arctic Ice Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!