Navigating the Night Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to the Northern Constellations
Related Articles: Navigating the Night Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to the Northern Constellations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Night Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to the Northern Constellations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Night Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to the Northern Constellations
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Night Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to the Northern Constellations
- 3.1 The Northern Hemisphere’s Celestial Canvas
- 3.2 A Brief History of Constellations
- 3.3 Navigating the Night Sky with Constellations
- 3.4 Identifying Northern Constellations
- 3.5 The Significance of Northern Constellations
- 3.6 Northern Constellations: A Closer Look
- 3.7 FAQs about Northern Constellations
- 3.8 Tips for Observing Northern Constellations
- 3.9 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Night Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to the Northern Constellations
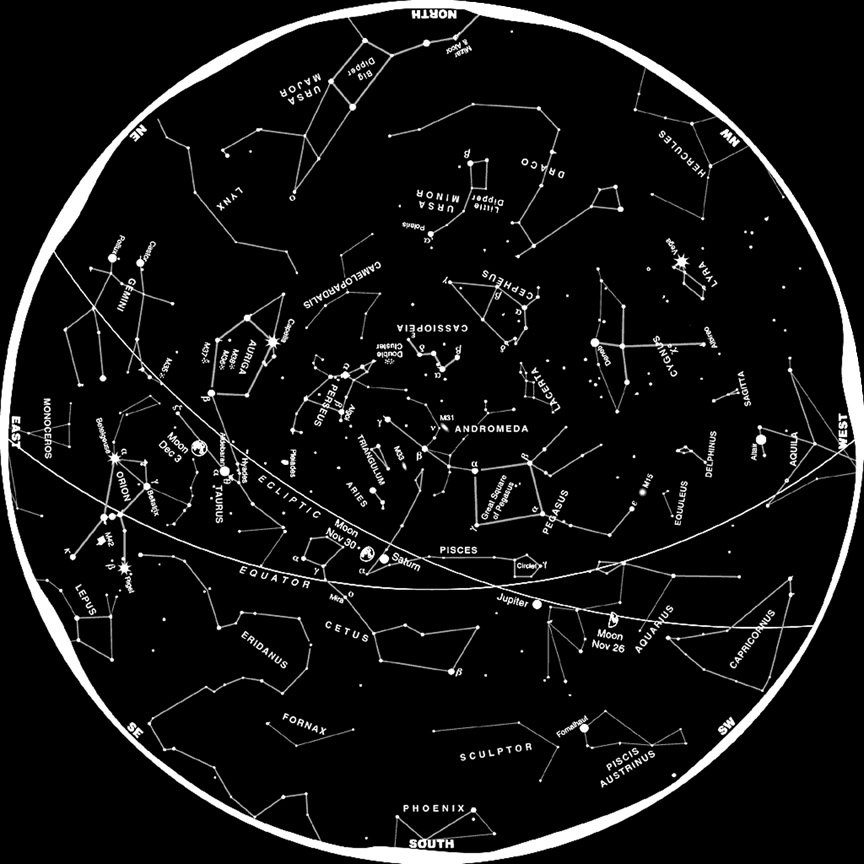
The night sky, a vast expanse of darkness punctuated by twinkling stars, has captivated humanity for millennia. From ancient civilizations to modern-day stargazers, the celestial tapestry has inspired awe, wonder, and a desire to understand the universe’s mysteries. One way to unravel this cosmic puzzle is through the study of constellations, patterns of stars that have been recognized and named across cultures for centuries. This article will delve into the fascinating world of northern constellations, exploring their history, significance, and how to identify them in the night sky.
The Northern Hemisphere’s Celestial Canvas
The northern hemisphere boasts a unique set of constellations, visible throughout the year, each with its own story and significance. These celestial patterns have been used for navigation, timekeeping, and even storytelling for millennia. Understanding the constellations of the northern hemisphere offers a glimpse into our cosmic neighborhood and a deeper appreciation for the universe’s vastness.
A Brief History of Constellations
The practice of recognizing star patterns dates back to ancient civilizations. Early cultures, such as the Egyptians, Babylonians, and Greeks, used constellations to track time, predict seasons, and guide their navigation. These celestial formations were often associated with myths, legends, and deities, creating a rich tapestry of cultural and historical significance.
For example, the constellation Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is one of the most recognizable constellations in the northern hemisphere. Its seven brightest stars form a distinctive dipper shape, which has been used for navigation for centuries. In Greek mythology, Ursa Major represents Callisto, a nymph transformed into a bear by the goddess Hera. This story, along with many others, highlights the deep connection between constellations and human storytelling.
Navigating the Night Sky with Constellations
Constellations serve as valuable tools for navigating the night sky. By identifying these celestial patterns, stargazers can locate specific stars and planets, understand the movement of celestial objects, and even determine their latitude.
For example, Polaris, the North Star, is located at the end of the handle of Ursa Minor, also known as the Little Dipper. This star, which appears nearly stationary in the sky, has been used as a navigational aid for centuries. By finding Polaris, one can determine true north, a crucial skill for sailors, explorers, and anyone venturing into unfamiliar territory.
Identifying Northern Constellations
Learning to identify constellations can be an enjoyable and rewarding experience. Several resources can aid in this endeavor:
- Star Charts and Apps: Star charts, both printed and digital, provide detailed maps of the night sky, showcasing constellations and their prominent stars. Mobile apps, such as Stellarium and SkySafari, offer interactive star charts that allow users to explore the night sky from any location and time.
- Observatory Visits: Planetariums and observatories often host stargazing events and presentations, providing expert guidance on identifying constellations and learning about their history and significance.
- Online Resources: Websites and online communities dedicated to astronomy offer a wealth of information on constellations, including detailed descriptions, star charts, and interactive tools.
The Significance of Northern Constellations
Beyond their historical and navigational value, northern constellations hold immense cultural and scientific significance:
- Cultural Heritage: Constellations have been woven into the fabric of human culture for millennia, shaping our understanding of the universe and inspiring art, literature, and mythology.
- Scientific Research: Constellations serve as reference points for astronomers, enabling them to study and map the vastness of the universe. By observing the movement and properties of stars within constellations, scientists can gain insights into the formation, evolution, and composition of celestial objects.
- Inspiration and Wonder: The beauty and mystery of constellations continue to inspire awe and wonder in people of all ages. Observing these celestial patterns reminds us of our place in the universe and encourages us to explore the vastness of space.
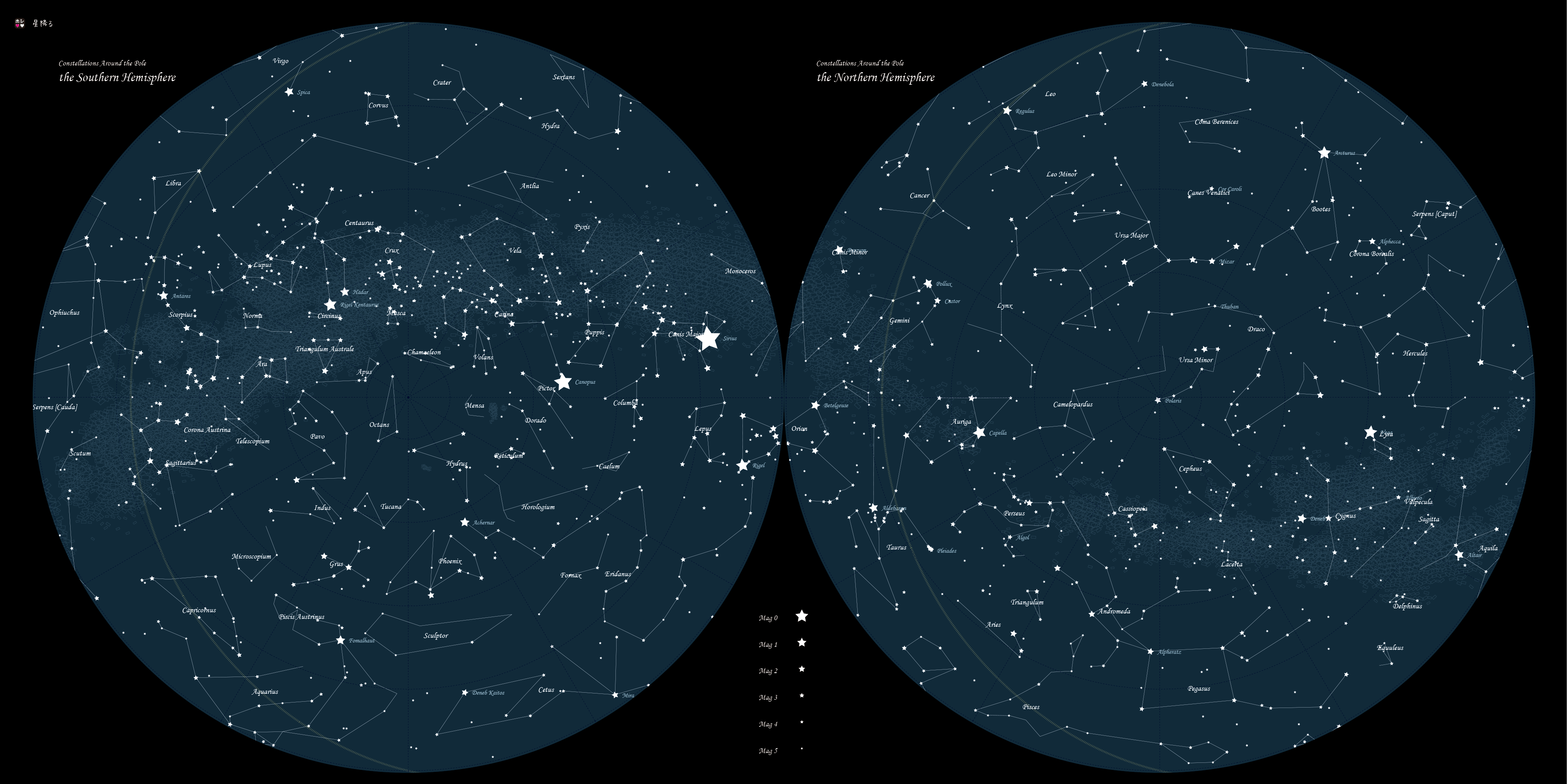
Northern Constellations: A Closer Look
Now, let’s delve into some of the most prominent northern constellations:
Ursa Major (The Great Bear)
As mentioned earlier, Ursa Major is one of the most recognizable constellations in the northern hemisphere. Its seven brightest stars form a distinctive dipper shape, with the two stars at the end of the dipper’s bowl pointing towards Polaris, the North Star. Ursa Major is circumpolar, meaning it never sets below the horizon for observers in the northern hemisphere.
Ursa Minor (The Little Bear)
Ursa Minor, the Little Bear, is located near Ursa Major. It is a smaller constellation, with its brightest star, Polaris, marking the end of its handle. Polaris is a crucial navigational star, as it remains nearly stationary in the sky, pointing towards true north.
Cassiopeia (The Queen)
Cassiopeia is a constellation shaped like a "W" or "M," depending on its position in the sky. It is located near Ursa Major and Polaris, and its distinctive shape makes it easy to identify. In Greek mythology, Cassiopeia represents a vain queen who boasted about her beauty, leading to her punishment by the gods.
Cepheus (The King)
Cepheus is a constellation located near Cassiopeia. It is a less prominent constellation, but its shape resembles a house or a pyramid. In Greek mythology, Cepheus represents the king of Ethiopia, the husband of Cassiopeia.
Draco (The Dragon)
Draco is a long, winding constellation that wraps around Ursa Minor. It is a faint constellation, but its distinctive shape makes it easy to identify. In Greek mythology, Draco represents a dragon that guarded the golden apples of the Hesperides.
Cygnus (The Swan)
Cygnus is a constellation shaped like a cross, with its brightest star, Deneb, marking the tail of the swan. It is located near the Milky Way, and its distinctive shape makes it easy to identify. In Greek mythology, Cygnus represents a swan that was transformed by the gods.
Lyra (The Lyre)
Lyra is a small but bright constellation located near Cygnus. It is shaped like a harp or a lyre, with its brightest star, Vega, marking the top of the lyre. In Greek mythology, Lyra represents a lyre played by the musician Orpheus.
Perseus (The Hero)
Perseus is a constellation located near Cassiopeia. It is a large constellation with a distinctive shape that resembles a man holding a sword. In Greek mythology, Perseus represents a hero who slew the Gorgon Medusa.
Andromeda (The Princess)
Andromeda is a constellation located near Perseus. It is a large and prominent constellation, with its brightest star, Alpheratz, marking the head of the princess. In Greek mythology, Andromeda represents a princess who was chained to a rock as a sacrifice to a sea monster.
Pegasus (The Winged Horse)
Pegasus is a constellation located near Andromeda. It is a large and prominent constellation, with its four brightest stars forming a square shape that represents the horse’s body. In Greek mythology, Pegasus represents a winged horse that sprang from the blood of Medusa.
FAQs about Northern Constellations
Q: How many constellations are there in the northern hemisphere?
A: There are 88 officially recognized constellations in the entire celestial sphere, but the number visible from the northern hemisphere varies depending on the time of year and location.
Q: Are the constellations static or do they change over time?
A: While the constellations appear to be fixed patterns, the stars within them are constantly moving. Due to their immense distances and slow movement, these shifts are not noticeable in a human lifetime. However, over thousands of years, the constellations will gradually change shape.
Q: What is the best time of year to observe northern constellations?
A: The best time to observe northern constellations is during the winter months when the nights are longer and the sky is clearer. However, many constellations are visible throughout the year, and the best time to observe specific constellations depends on their position in the sky.
Q: Can constellations be seen from any location on Earth?
A: No. The visibility of constellations depends on the observer’s latitude. Constellations near the celestial poles are visible year-round, while those near the celestial equator are only visible during specific seasons.
Tips for Observing Northern Constellations
- Find a dark location: Light pollution from cities and towns can obscure faint stars, making it difficult to observe constellations. Seek out a location away from artificial lights for optimal stargazing.
- Use a star chart or app: A star chart or app will help you identify constellations and their prominent stars. These tools also provide information on the visibility of constellations at different times of year.
- Start with the most recognizable constellations: Begin by identifying the most prominent constellations, such as Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, and Orion. Once you have located these, you can use them as reference points to find other constellations.
- Be patient and persistent: Learning to identify constellations takes time and practice. Don’t be discouraged if you don’t see everything right away. With patience and persistence, you will gradually become familiar with the night sky.
Conclusion
Exploring the constellations of the northern hemisphere is a journey of discovery, connecting us to the rich history of astronomy, inspiring a sense of wonder, and deepening our understanding of the universe. From ancient myths to modern-day scientific research, these celestial patterns have played a vital role in human history and continue to captivate our imaginations. By learning to identify and appreciate these celestial formations, we can unlock a new perspective on our place in the cosmos, fostering a deeper connection to the universe around us.

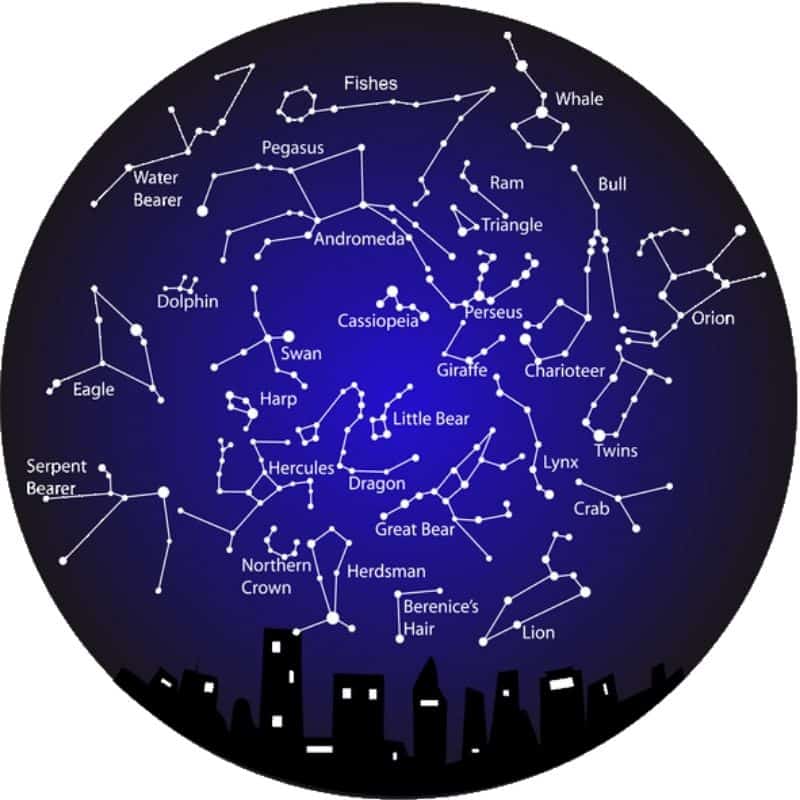

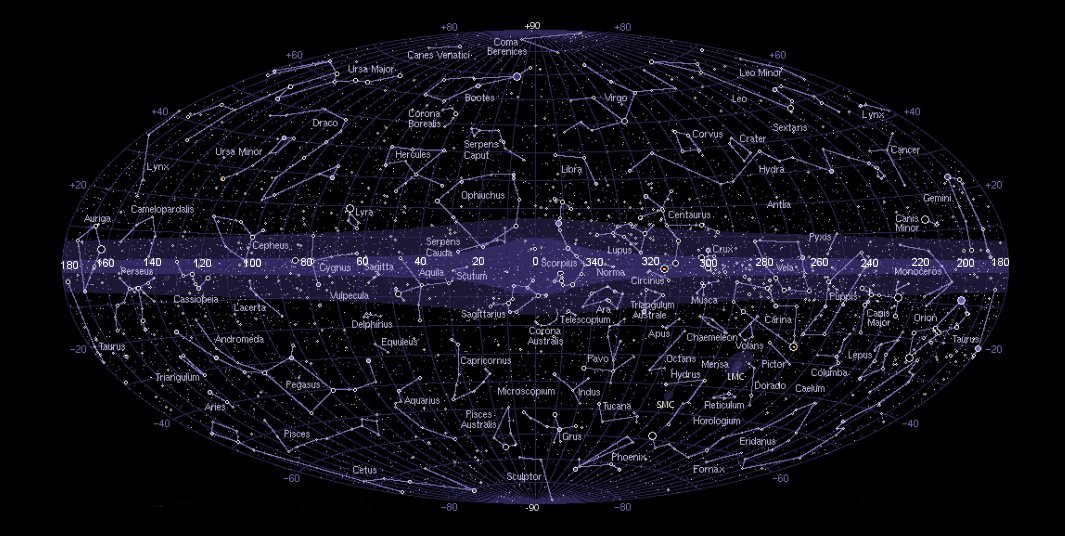
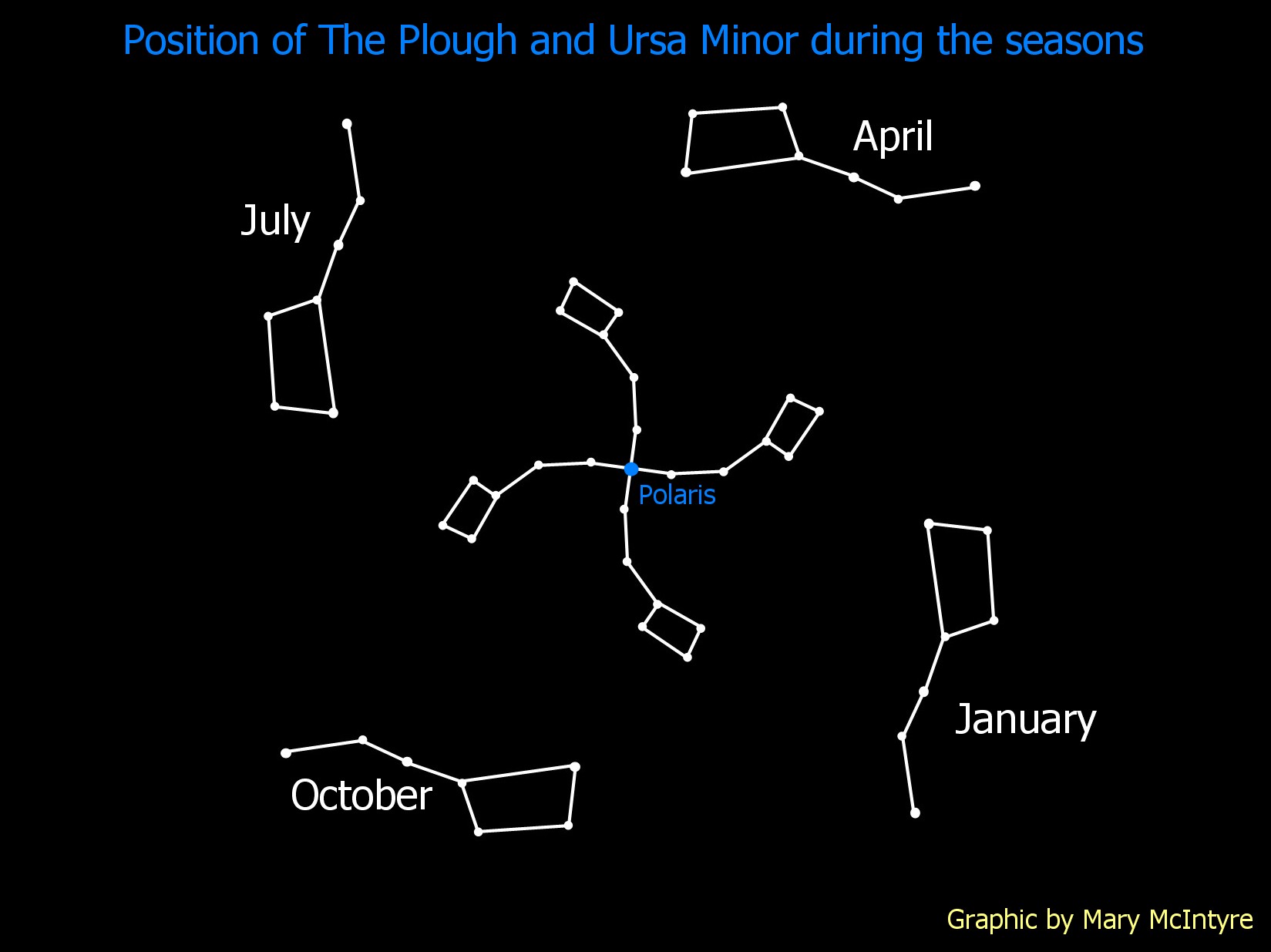

![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Night Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to the Northern Constellations. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!