Navigating the Climate Tapestry of Iran: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Iranian Weather Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Climate Tapestry of Iran: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Iranian Weather Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Climate Tapestry of Iran: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Iranian Weather Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Climate Tapestry of Iran: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Iranian Weather Map
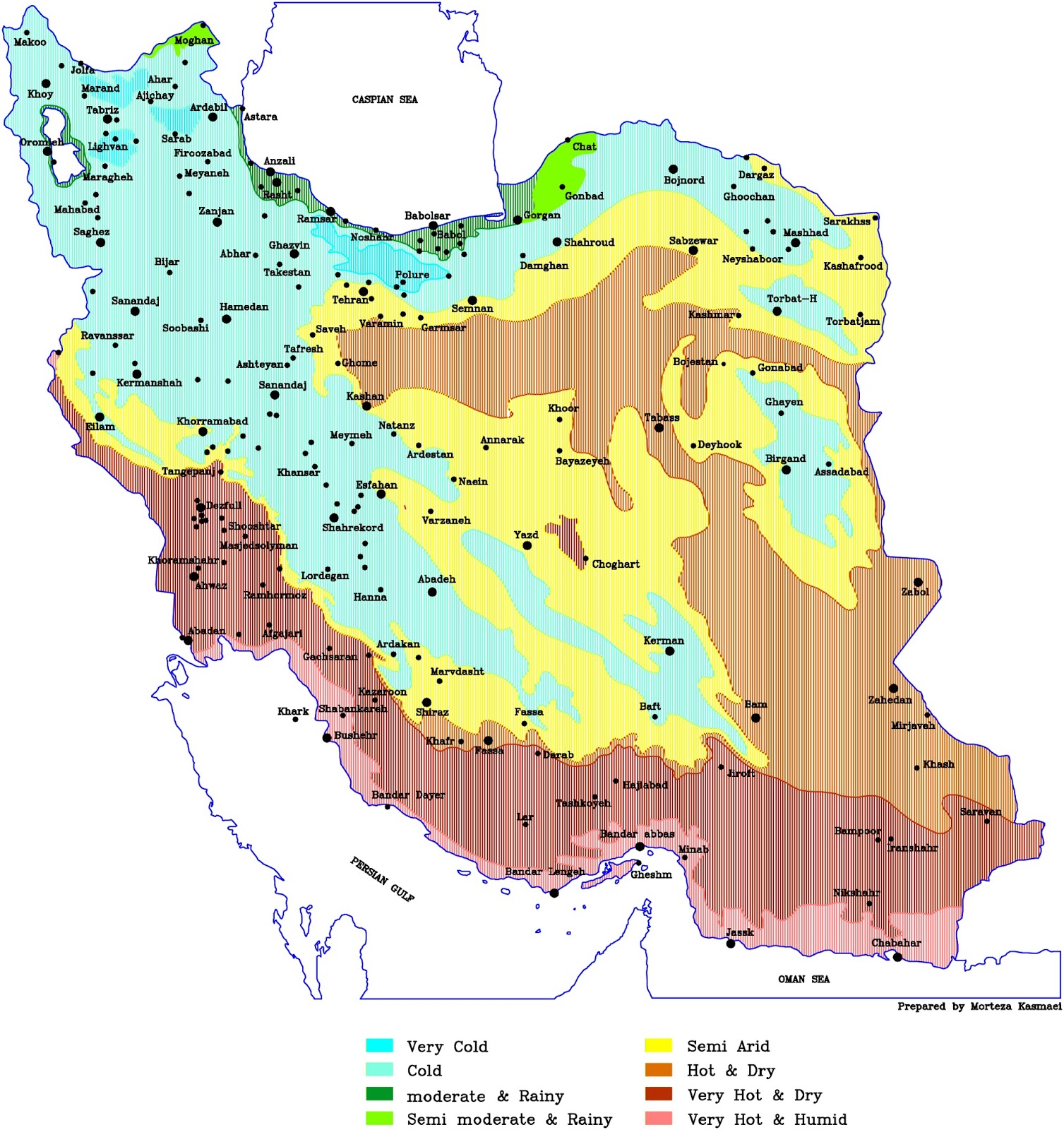
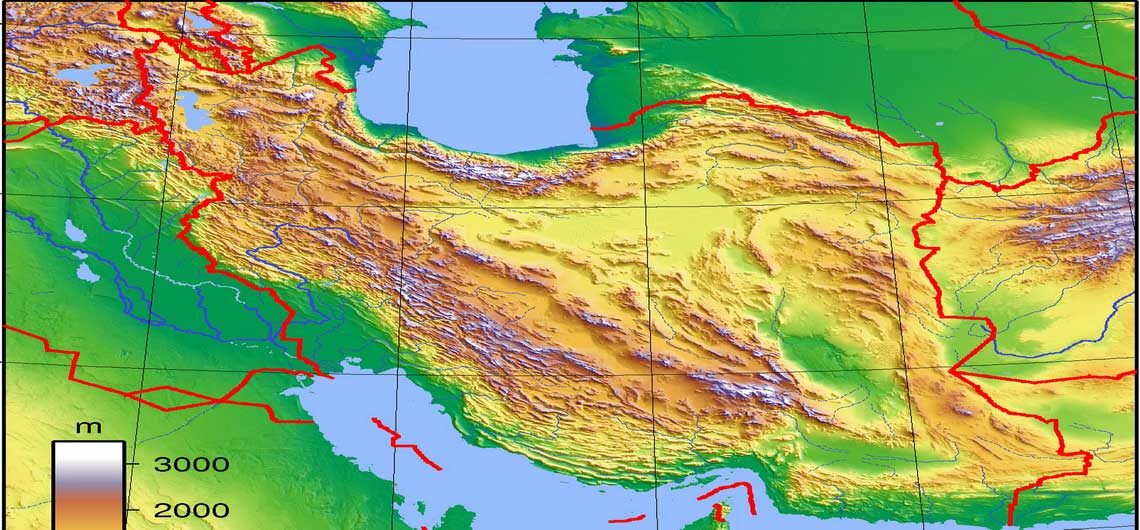
Iran, a land of ancient civilizations and breathtaking landscapes, is also a country with a remarkably diverse climate. From the scorching deserts of the south to the snow-capped peaks of the Zagros Mountains, the weather in Iran varies dramatically across its vast expanse. Understanding this complex tapestry of climate is crucial for anyone planning a trip to Iran, whether for leisure, business, or research. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the intricacies of Iranian weather by exploring the key features and factors that shape the weather patterns across the country.
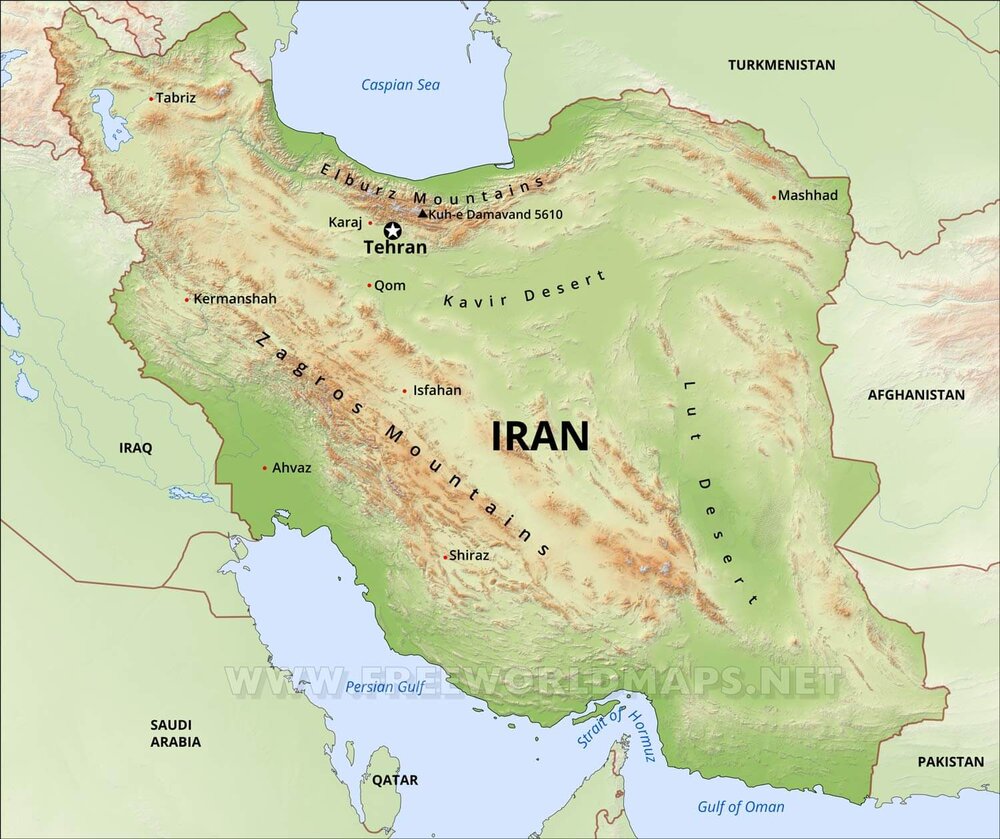
Understanding the Geographical Influences:
Iran’s unique geography plays a pivotal role in shaping its diverse weather patterns. The country is situated in a strategically important location, bordering the Caspian Sea to the north, the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman to the south, and with mountainous terrain dominating its central and western regions. These geographical features, coupled with the influence of major atmospheric systems, create a complex interplay of weather conditions.
The Caspian Sea’s Influence:
The Caspian Sea, the world’s largest inland body of water, exerts a significant moderating influence on Iran’s northern regions. The presence of the Caspian Sea results in a humid, subtropical climate along the northern coastal plains, with warm, wet summers and mild, wet winters. This area experiences the highest rainfall in Iran, often exceeding 1000 millimeters annually.
The Zagros Mountains: A Barrier to Moisture:
The Zagros Mountains, stretching across western and central Iran, act as a formidable barrier to moisture-laden air masses from the west. This mountainous terrain significantly influences precipitation patterns, creating a rain shadow effect on the eastern side of the mountains. As a result, the eastern regions experience a much drier climate than the western regions.
The Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman: A Source of Heat and Humidity:
The Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman, located to the south of Iran, are major sources of heat and humidity for the country. The proximity of these warm bodies of water contributes to the hot, arid climate prevalent in southern Iran. The region experiences high temperatures, especially during the summer months, with minimal rainfall throughout the year.
The Influence of Atmospheric Systems:
Iran’s weather is also influenced by major atmospheric systems, including the Mediterranean low-pressure system, the Siberian high-pressure system, and the Indian monsoon. The Mediterranean low-pressure system brings moisture and rainfall to the western and northwestern regions of Iran during the winter months. The Siberian high-pressure system, originating from the north, brings cold and dry air to Iran during the winter, leading to snow and freezing temperatures in mountainous areas. The Indian monsoon, while having a less direct impact compared to other systems, can bring heavy rainfall to the southeastern regions of Iran during the summer months.
Delving Deeper into the Weather Map:
The Iranian weather map provides a visual representation of the various weather conditions across the country. It typically includes information such as temperature, precipitation, wind speed and direction, cloud cover, and other relevant meteorological data. Understanding the different symbols and color codes used on the weather map is crucial for interpreting the current and predicted weather conditions.
Interpreting the Weather Map:
- Temperature: The weather map uses different color gradients to represent temperature variations across Iran. Typically, warmer temperatures are depicted in shades of red and orange, while colder temperatures are shown in shades of blue and purple.
- Precipitation: Precipitation is represented by various symbols, such as raindrops, snowflakes, or hail. The intensity of precipitation is often indicated by the size and density of the symbols.
- Wind Speed and Direction: Wind direction is usually depicted by arrows, with the arrowhead pointing in the direction from which the wind is blowing. Wind speed is often represented by the length or thickness of the arrow.
- Cloud Cover: Cloud cover is represented by different symbols, with a completely filled circle indicating full cloud cover and an empty circle indicating clear skies.
- Other Meteorological Data: The weather map may also include additional information, such as humidity levels, visibility, and sunrise and sunset times.
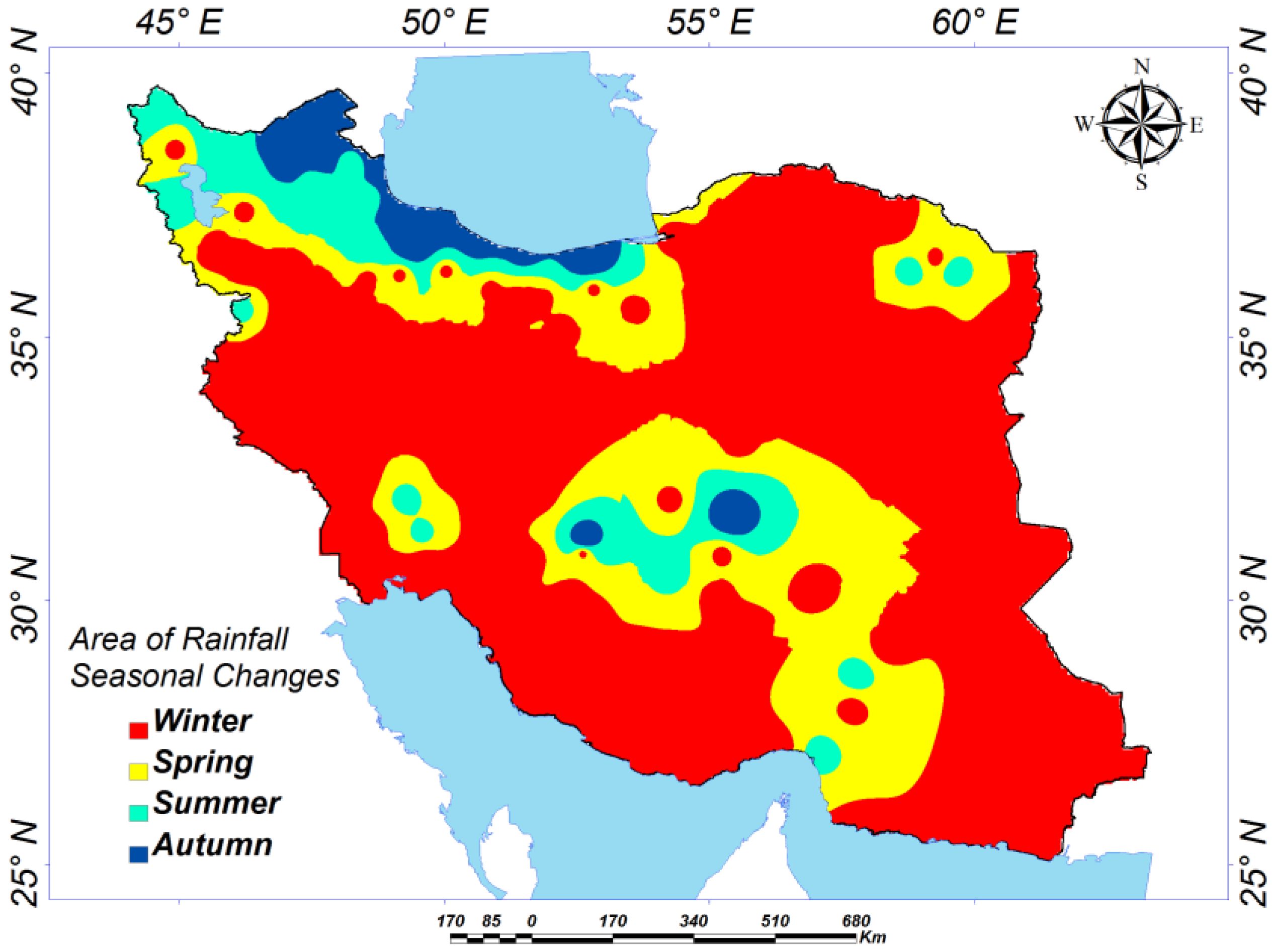
Exploring the Seasonal Variations:
Winter (December – February):
- Northern Regions: Mild and wet with occasional snowfall.
- Central and Western Regions: Cold and snowy, with temperatures dropping below freezing in mountainous areas.
- Southern Regions: Relatively mild with occasional rainfall.
Spring (March – May):
- Northern Regions: Gradually warming with occasional showers.
- Central and Western Regions: Temperatures rise, with snow melting in lower elevations.
- Southern Regions: Hot and dry, with increasing temperatures.
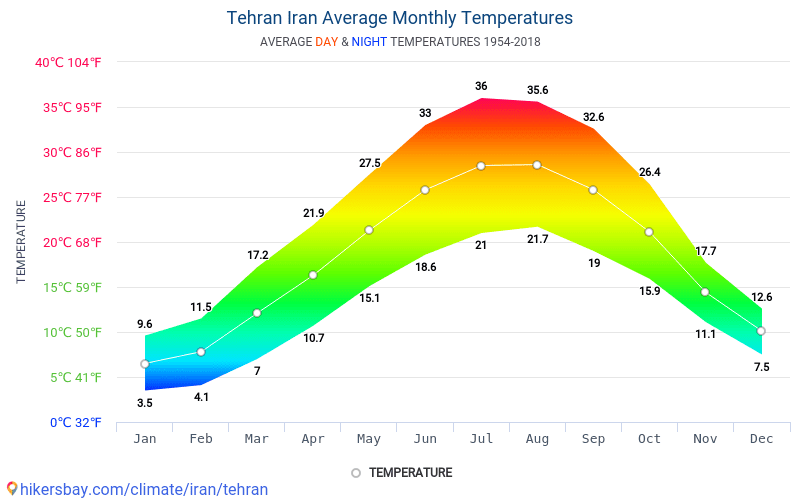
Summer (June – August):
- Northern Regions: Hot and humid with occasional thunderstorms.
- Central and Western Regions: Extremely hot and dry with temperatures exceeding 40 degrees Celsius in some areas.
- Southern Regions: Extremely hot and humid with temperatures often exceeding 50 degrees Celsius.
Autumn (September – November):
- Northern Regions: Mild and sunny with occasional showers.
- Central and Western Regions: Mild and sunny with temperatures gradually decreasing.
- Southern Regions: Warm and dry with decreasing temperatures.
Navigating the Weather Challenges:
Extreme Heat: The extreme heat experienced in southern Iran during the summer months can pose a significant health risk. It is essential to stay hydrated, avoid strenuous activities during the hottest hours, and seek shade whenever possible.
Cold and Snow: The cold and snowy conditions in the mountainous regions of Iran during the winter months can make travel difficult and dangerous. It is crucial to check weather forecasts, prepare for winter driving conditions, and carry appropriate winter gear.
Rainfall and Floods: Iran experiences significant rainfall during the winter months, particularly in the western and northwestern regions. This can lead to flash floods and landslides, especially in mountainous areas. It is important to stay informed about weather forecasts and avoid areas prone to flooding.
Desert Conditions: The arid desert conditions in southern Iran can be challenging for travelers. It is essential to carry sufficient water, wear appropriate clothing, and avoid traveling alone in remote areas.
Benefits of Understanding the Iranian Weather Map:
- Informed Travel Planning: Understanding the weather patterns in Iran allows travelers to plan their trips accordingly, choosing the best time to visit different regions and packing appropriate clothing and gear.
- Enhanced Safety: Awareness of potential weather hazards such as extreme heat, cold, floods, and desert conditions can help travelers take necessary precautions and ensure their safety.
- Improved Research and Analysis: Researchers and scientists can utilize weather data to study climate change, analyze agricultural yields, and understand the impact of weather on various sectors of the Iranian economy.
- Effective Disaster Management: Understanding weather patterns is crucial for disaster management agencies to prepare for and respond to natural disasters such as floods, droughts, and storms.
FAQs about the Iranian Weather Map:
Q: What is the best time to visit Iran?
A: The best time to visit Iran depends on the specific region and your interests. Spring (March – May) and autumn (September – November) are generally considered the most pleasant times to visit, offering mild temperatures and comfortable conditions.
Q: How reliable are the Iranian weather forecasts?
A: The accuracy of Iranian weather forecasts varies depending on the region and the forecasting agency. However, reputable weather websites and apps typically provide reliable forecasts, especially for major cities and tourist destinations.
Q: What are the most common weather hazards in Iran?
A: The most common weather hazards in Iran include extreme heat, cold and snow, rainfall and floods, and desert conditions.
Q: How can I stay informed about weather conditions in Iran?
A: You can stay informed about weather conditions in Iran by checking reputable weather websites and apps, such as the Iranian Meteorological Organization website (www.irimo.ir) or international weather services like AccuWeather or The Weather Channel.
Tips for Utilizing the Iranian Weather Map:
- Check the date and time of the forecast: Ensure that the weather map you are using is up-to-date and relevant to your travel dates.
- Pay attention to the symbols and color codes: Familiarize yourself with the different symbols and color codes used on the weather map to interpret the information accurately.
- Consider the specific region you are visiting: The weather can vary significantly across different regions of Iran. Check the forecast for the specific area you are planning to visit.
- Be prepared for unexpected changes: Weather conditions can change rapidly in Iran. It is always advisable to pack layers and be prepared for a range of weather possibilities.
Conclusion:
The Iranian weather map is a valuable tool for understanding the diverse and complex climate of Iran. By comprehending the various factors that influence weather patterns, travelers, researchers, and policymakers can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and harness the unique climatic features of this fascinating country. From the humid coastal plains to the arid deserts, the Iranian weather map provides a window into the dynamic and ever-changing climate of this ancient land.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Climate Tapestry of Iran: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Iranian Weather Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!