Navigating the Arteries of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Petroleum Pipeline Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Arteries of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Petroleum Pipeline Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Arteries of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Petroleum Pipeline Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Arteries of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Petroleum Pipeline Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Arteries of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Petroleum Pipeline Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Significance of Petroleum Pipeline Maps
- 3.2 Key Components of a Comprehensive Petroleum Pipeline Map
- 3.3 Benefits of Using Petroleum Pipeline Maps
- 3.4 Navigating the Global Pipeline Network: A Case Study
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Petroleum Pipeline Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Use of Petroleum Pipeline Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Vital Infrastructure for a Globalized World
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Arteries of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Petroleum Pipeline Maps
![US Pipeline Map Printable [Pipeline Map of US]](https://unitedstatesmaps.org/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/us-pipeline-map.jpg)
The intricate network of pipelines crisscrossing the globe serves as the backbone of the global petroleum industry, facilitating the transportation of crude oil and refined products from source to market. These pipelines, often referred to as the "arteries of energy," play a pivotal role in ensuring the uninterrupted flow of fuel that powers our modern world. Understanding the complexities of this network requires a comprehensive grasp of the information presented in petroleum pipeline maps.
Understanding the Significance of Petroleum Pipeline Maps
Petroleum pipeline maps are not merely static representations of infrastructure. They are dynamic tools offering valuable insights into the global energy landscape. These maps provide a visual overview of:
- Pipeline Infrastructure: Detailed information on pipeline routes, sizes, and capacities, allowing for an assessment of the overall capacity and efficiency of the network.
- Production and Consumption Centers: Identifying key oil and gas production regions, major refineries, and crucial consumption hubs, revealing the flow of energy across continents.
- Interconnectivity and Dependence: Highlighting the intricate connections between different regions and countries, emphasizing the interconnectedness of the global energy market.
- Potential Bottlenecks and Vulnerabilities: Revealing potential chokepoints within the network, identifying areas where disruptions could significantly impact energy supply.
- Environmental Considerations: Mapping pipeline routes in relation to sensitive ecosystems, highlighting potential environmental impacts and informing responsible development strategies.
Key Components of a Comprehensive Petroleum Pipeline Map
A comprehensive petroleum pipeline map goes beyond simply depicting pipeline routes. It encompasses a wealth of information presented in a clear and accessible manner. Essential components include:
- Pipeline Routes: Clearly defined routes, often color-coded to differentiate between crude oil, refined products, and natural gas pipelines.
- Pipeline Capacities: Indicating the flow rate and volume of oil or gas that can be transported through each pipeline, providing insights into operational efficiency.
- Pipeline Ownership and Operators: Identifying the companies responsible for the construction, maintenance, and operation of each pipeline, highlighting the complex web of stakeholders in the industry.
- Pipeline Interconnections: Displaying points where pipelines connect, illustrating the flow of oil and gas from production to consumption.
- Key Infrastructure: Marking major oil and gas fields, refineries, storage terminals, and key consumption centers, providing a complete picture of the energy value chain.
- Geographic Context: Integrating the pipeline network with detailed geographical features, including mountains, rivers, and urban areas, allowing for a better understanding of potential challenges and opportunities.
Benefits of Using Petroleum Pipeline Maps
The use of petroleum pipeline maps offers numerous benefits for various stakeholders in the energy industry:
- Resource Management: Providing a visual representation of the global energy landscape, enabling efficient resource allocation and planning for future infrastructure development.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential vulnerabilities within the pipeline network, allowing for proactive measures to mitigate risks and ensure uninterrupted supply.
- Environmental Planning: Facilitating the integration of environmental considerations into pipeline development and operation, minimizing potential impacts on ecosystems.
- Economic Development: Supporting strategic decision-making by governments and businesses, fostering investments in infrastructure and economic growth.
- Public Awareness: Promoting transparency and public understanding of the complex energy infrastructure, fostering informed discussions about energy policy and sustainability.
Navigating the Global Pipeline Network: A Case Study
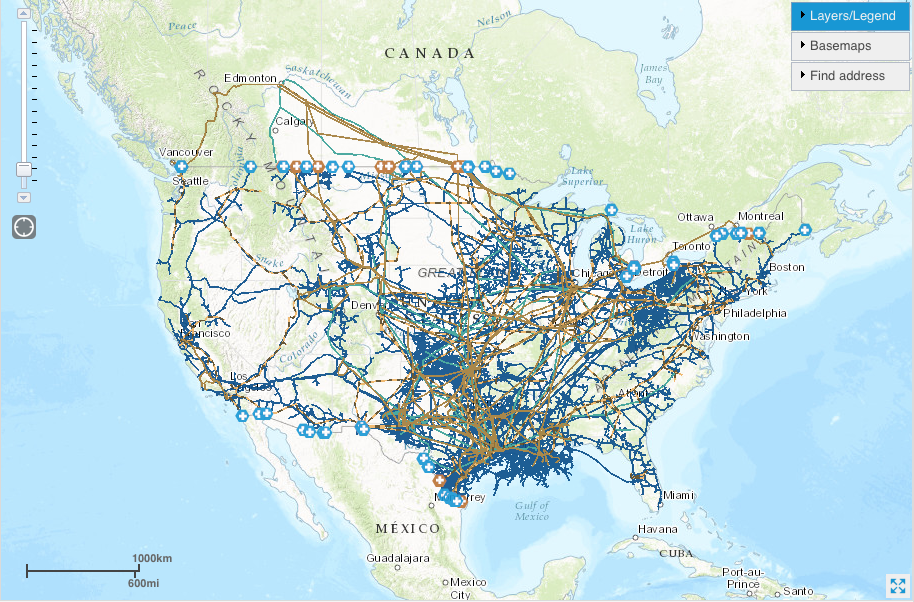
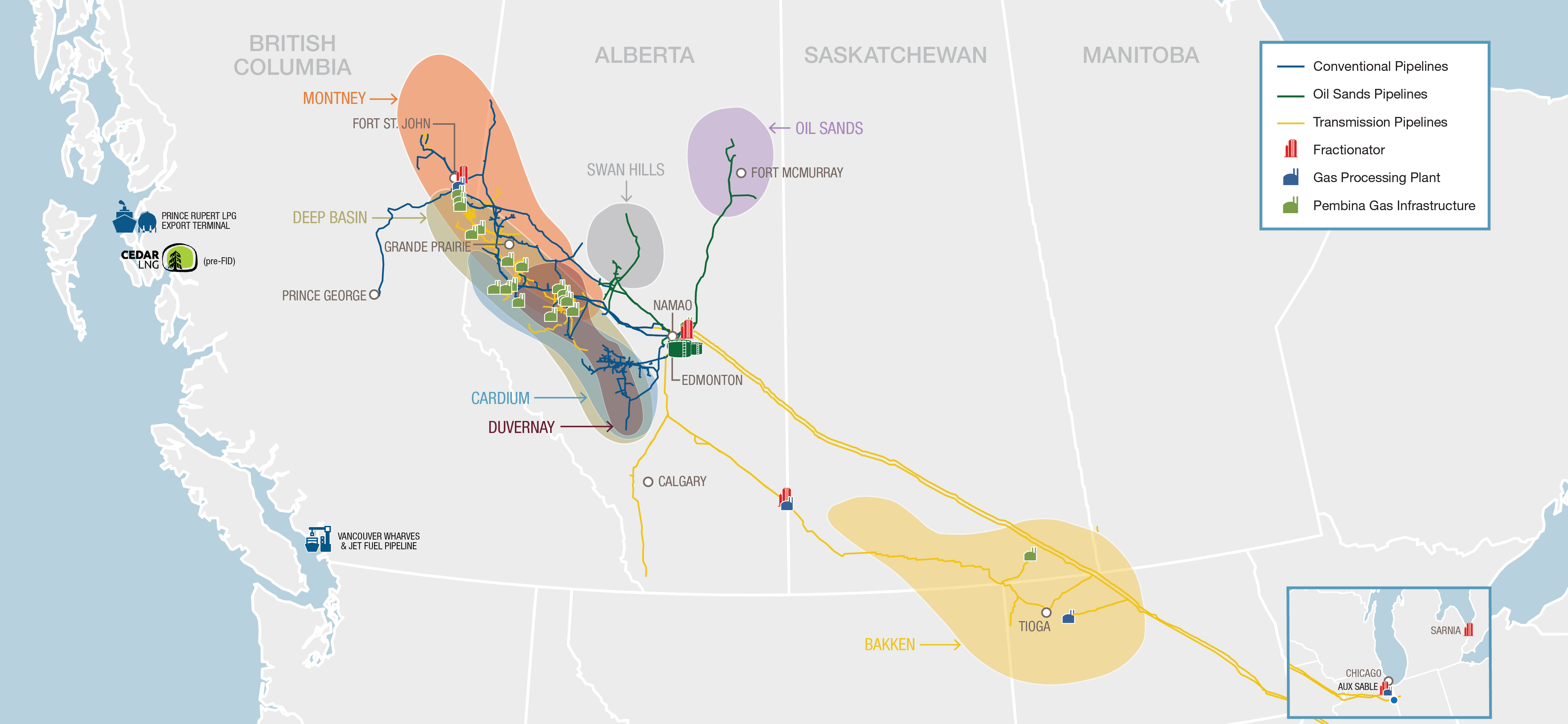
To illustrate the practical application of petroleum pipeline maps, let’s examine the North American pipeline network. This network, spanning thousands of miles, transports vast quantities of oil and gas across the continent, connecting production regions in Canada and the United States to major refineries and consumption centers.
A detailed map of this network reveals crucial insights:
- Key Production Hubs: The Canadian oil sands and the Bakken shale play in North Dakota are major sources of crude oil, feeding the network’s pipelines.
- Refining Centers: Texas and the Gulf Coast region boast significant refining capacity, processing crude oil into gasoline, diesel, and other products.
- Interconnectivity: Pipelines connect these production and refining centers, forming a complex network that ensures the smooth flow of energy.
- Environmental Concerns: Pipeline routes often traverse sensitive ecosystems, raising concerns about potential spills and environmental impacts.
By studying this map, policymakers, energy companies, and environmental groups can better understand the challenges and opportunities associated with the North American pipeline network, fostering informed decision-making and sustainable development.
Frequently Asked Questions about Petroleum Pipeline Maps
1. What are the different types of pipelines used in the petroleum industry?
The petroleum industry utilizes various types of pipelines, each designed for specific purposes and transporting different types of hydrocarbons:
- Crude Oil Pipelines: Transporting raw, unrefined oil from production sites to refineries.
- Product Pipelines: Carrying refined petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel, from refineries to distribution terminals.
- Natural Gas Pipelines: Transporting natural gas from production sites to processing plants and distribution networks.
2. How are pipeline routes determined?
Pipeline routes are determined through a complex process involving:
- Geological Surveys: Identifying suitable terrain and soil conditions for pipeline construction.
- Environmental Assessments: Evaluating potential impacts on ecosystems, wildlife, and communities.
- Economic Feasibility Studies: Assessing the cost-effectiveness of different routes.
- Regulatory Approvals: Obtaining permits and approvals from relevant authorities.
3. What are the environmental risks associated with pipelines?
Pipelines pose potential environmental risks, including:
- Oil Spills: Accidents can lead to oil spills, contaminating soil and water resources.
- Habitat Fragmentation: Pipeline construction can disrupt wildlife habitats and fragment ecosystems.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Pipeline leaks can release methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere.
4. How are pipelines regulated and monitored?
Pipelines are subject to stringent regulations and monitoring, including:
- Safety Standards: Compliance with industry safety standards to prevent accidents.
- Regular Inspections: Periodic inspections to ensure pipeline integrity and identify potential problems.
- Leak Detection Systems: Advanced technologies to detect leaks and minimize environmental damage.
5. What is the future of the petroleum pipeline network?
The future of the petroleum pipeline network is uncertain, influenced by factors such as:
- Shifting Energy Demand: Growing demand for renewable energy sources could reduce the need for oil and gas pipelines.
- Technological Advancements: New technologies, such as carbon capture and storage, could reshape the energy landscape.
- Environmental Concerns: Increasing awareness of environmental impacts could lead to stricter regulations and alternative transportation methods.
Tips for Effective Use of Petroleum Pipeline Maps
- Consider the Scale: Select a map that provides the appropriate level of detail for your needs, whether it’s a global overview or a regional focus.
- Explore Data Layers: Utilize interactive maps with data layers that allow you to filter and analyze information based on specific criteria, such as pipeline capacity, ownership, or environmental sensitivities.
- Cross-Reference Data: Combine pipeline map data with other relevant information, such as production statistics, energy consumption patterns, and environmental regulations, for a more comprehensive understanding.
- Stay Updated: The petroleum pipeline network is constantly evolving, so ensure you are using the most up-to-date maps and data.
- Engage with Experts: Consult with experts in the field, such as pipeline engineers, energy analysts, and environmental specialists, to gain deeper insights and interpret map data effectively.
Conclusion: A Vital Infrastructure for a Globalized World
Petroleum pipeline maps are essential tools for understanding the global energy landscape, informing decision-making, and promoting responsible development. They provide a visual representation of the complex network of pipelines that transport oil and gas across continents, connecting production sites with refineries and consumption centers. By understanding the intricacies of this network, policymakers, energy companies, and environmental groups can work together to ensure a secure, efficient, and sustainable energy future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Arteries of Energy: A Comprehensive Look at Petroleum Pipeline Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!